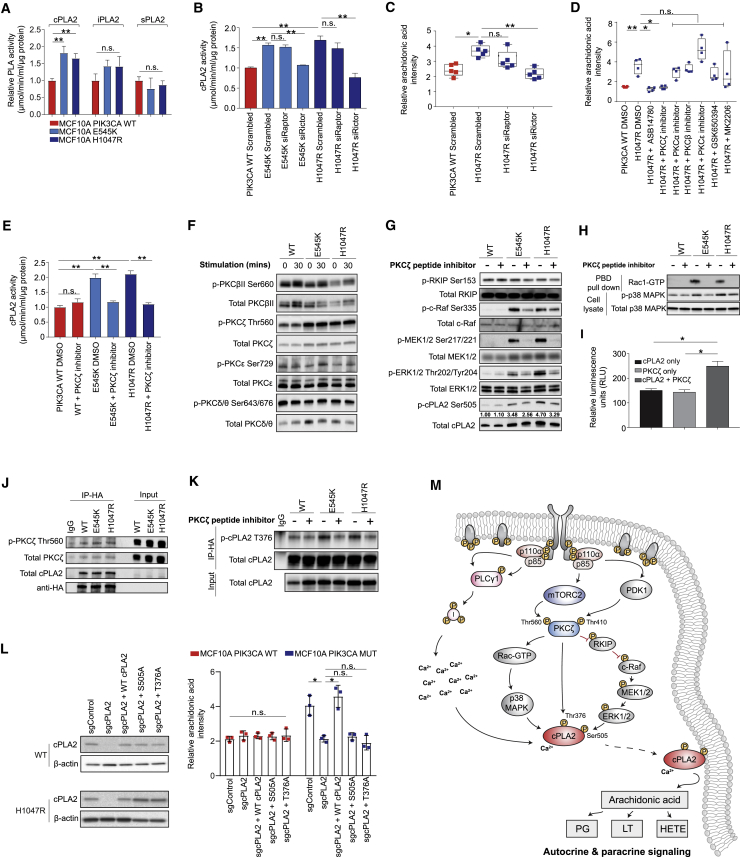
Figure 4.
Oncogenic PIK3CA Signaling Triggers cPLA2-Induced Arachidonic Acid Production
(A) Enzymatic activity of cPLA2, iPLA2, and sPLA2 in the MCF10A PIK3CA isogenic panel.
(B–D) cPLA2 activity (B) and AA levels (C and D) measured by REIMS in MCF10A H1047R PIK3CA MUT cells following RAPTOR or RICTOR siRNA-mediated knockdown (C), or treatment with 100 nM ASB14780, 1 μM each of PKCα, β, ε, or ζ peptide inhibitors, 250 μM GSK650394, or 150 nM MK2206 for 72 h (D). Cells were grown under exogenous FAF conditions.
(E) cPLA2 activity following PKCζ inhibition with 1 μM peptide inhibitor for 72 h.
(F and G) Immunoblot analysis of the MCF10A PIK3CA isogenic panel following growth factor deprivation for 16 h and 30 min stimulation with serum and growth factors (F) or PKCζ inhibition with 1 μM peptide inhibitor for 72 h (G).
(H) Immunoblot analysis of activated Rac-1 and p38 MAPK in the MCF10A PIK3CA isogenic panel following PKCζ inhibition with 1 μM peptide inhibitor for 72 h.
(I) In vitro kinase assay of 100 ng and 0.5 μg/μL purified PKCζ and cPLA2 proteins, respectively.
(J) Immunoblot analysis of anti-HA immunoprecipitates derived from HA-tagged cPLA2 transfected MCF10A PIK3CA WT and MUT cells.
(K) Immunoblot analysis of anti-HA immunoprecipitates derived from HA-tagged cPLA2 transfected MCF10A PIK3CA WT and MUT cells treated where indicated with 1 μM PKCζ peptide inhibitor for 48 h.
(L) AA levels across H1047R MUT cells with CRISPR knockout of PLA2G4A reconstituted with WT or phosphoresistant cPLA2 isoforms.
(M) Diagram summarizing the proposed model for PI3K-mTORC2-PKCζ and calcium-dependent activation of cPLA2, leading to a concomitant increase in AA and downstream eicosanoids. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of n = 3–6 biological replicates and are representative of at least two independent experiments. n.s., not significant; ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001. p values in (A) were calculated with unpaired, two tailed Student’s t test, and in (B)–(E), (I), and (L) with one-way ANOVA, followed by unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test with Bonferroni correction.