FIGURE 5.
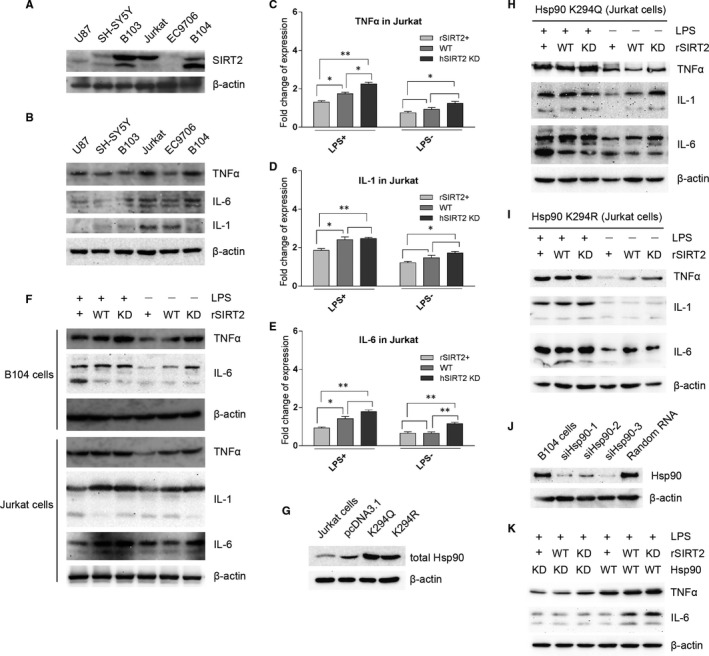
SIRT2 expression was examined in six cell lines. B103, B104 and Jurkat cells express SIRT2 (A). These cell lines were also tested for expression of TNFα, IL‐1 and IL‐6. The results showed that Jurkat cells express three cytokines and B104 cells express only TNFα and IL‐6 (B). qPCR for cytokine mRNA was performed in Jurkat cells (C‐E). rSIRT2 overexpression significantly reduced the mRNA levels of TNFα (C), IL‐1(D) and IL‐6(E) compared with hSIRT2 (siRNA‐III) knocked‐down, particularly for expression of cytokines under LPS stimulation (C‐E). In contrast, no significant change was observed between cells with hSIRT2 (siRNA‐III) knocked‐down and control cells for expression of IL‐1 under LPS stimulation (D), or between cells with rSIRT2 overexpression and control cells for expression of IL‐6 without LPS stimulation (E). qPCR was performed in triplicate plate for each sample, and data represent the mean ± SEM; t test, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. Protein expression level of cytokines in Jurkat and B104 cells with SIRT2 overexpression, SIRT2 knocked‐down or control was detected with or without LPS stimulation (F). rHSP90 mutants K294Q and K294R were transfected into Jurkat cells, and overexpression compared with the control cells and blank vector was confirmed by Western blot (G). The acetylation‐mimic mutant K294Q reversed the repression of cytokine expression mediated by rSIRT2 overexpression (H), except for IL‐1 and IL‐6 without LPS stimulation. Conversely, acetylation‐null mutant K294R effectively reversed up‐regulation of cytokine expression mediated by rSIRT2 knock‐down (I), except for TNFα without LPS stimulation. To knock‐down Hsp90 expression in B104 cells, three RNA fragments were measured. siHsp90‐3 showed the most effective knock‐down of Hsp90 (J). Hsp90 knock‐down reduced cytokine expression levels regardless of SIRT2 expression under LPS stimulation (K)
