FIGURE 1.
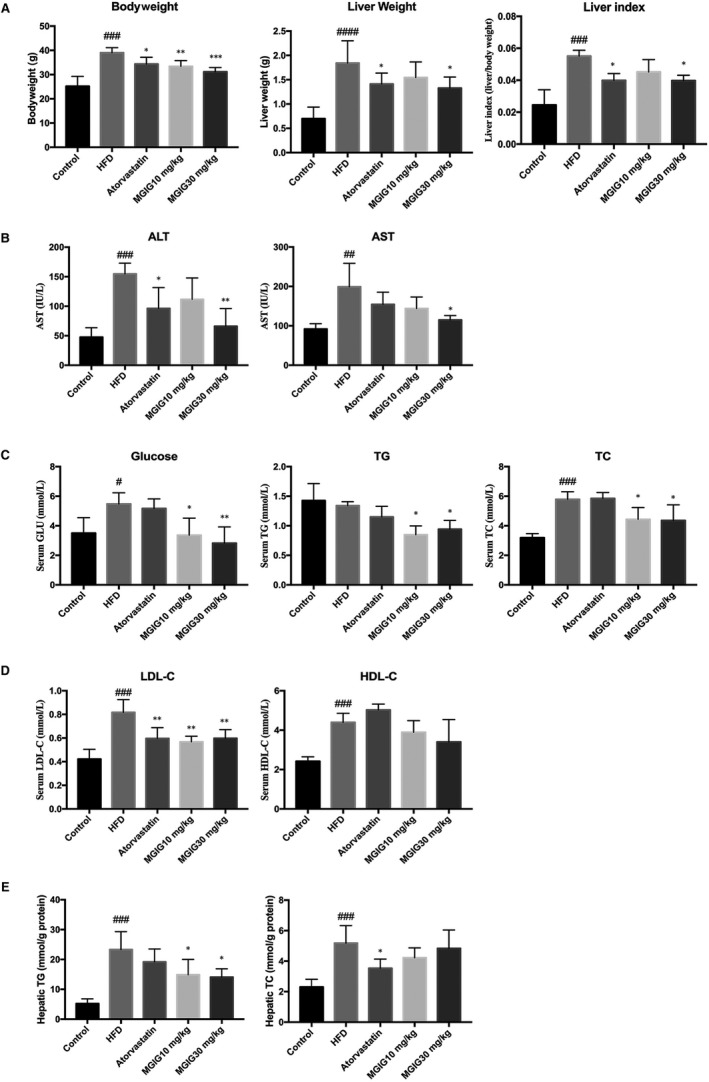
The protective effect of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MGIG) treatment on hepatic injury caused by high‐fat diet (HFD). The liver steatosis was induced by a HFD for 12 wk. The MGIG groups were intraperitoneally treated with MGIG (10 or 30 mg/kg) once a day for 6 wk since 7th week. The bodyweight, liver weight and the ratio of liver weight/bodyweight (A). The activities of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase in serum (AST; B). The serum levels of glucose, triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC; C). The serum levels of low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL‐C) and high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL‐C; D). The hepatic levels of triglyceride (TG) and total cholesterol (TC; E). The data were presented as means ± SDs. Compared with Control group: # P < .05, ## P < .01, ### P < .001. Compared with Model group: *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001 (n = 6)
