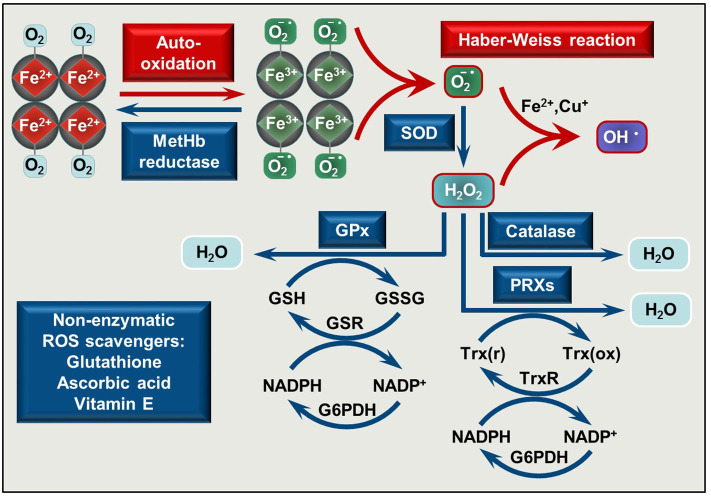
Figure 1.
Pro-oxidant and antioxidant mechanisms is RBCs. O2 binding to Hb initiates Hb auto-oxidation in which process metHb (Fe3+) and superoxide anion () are formed. MetHb is reduced by metHb reductase, while is converted to H2O2 by superoxide dismutase (SOD). In the presence of transition metals such as Fe2+ or Cu+ a reaction between and H2O2 occurs yielding hydroxyl radical (OH•) (Haber Weiss reaction). Catalase, glutathione peroxidases (GPx), and peroxiredoxins (PRXs) decompose H2O2. The antioxidant system is completed with non-enzymatic low molecular weight scavengers, such as glutathione, ascorbic acid, and vitamin E. SOD, superoxide dismutase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; PRXs, peroxiredoxins; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, glutathione disulfide; GSR, glutathione-disulfide reductase; NADP+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, reduced NADP; G6PDH, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; Trx(r), reduced thioredoxin; Trx(ox), oxidized thioredoxin; TrxR, thioredoxin reductase.