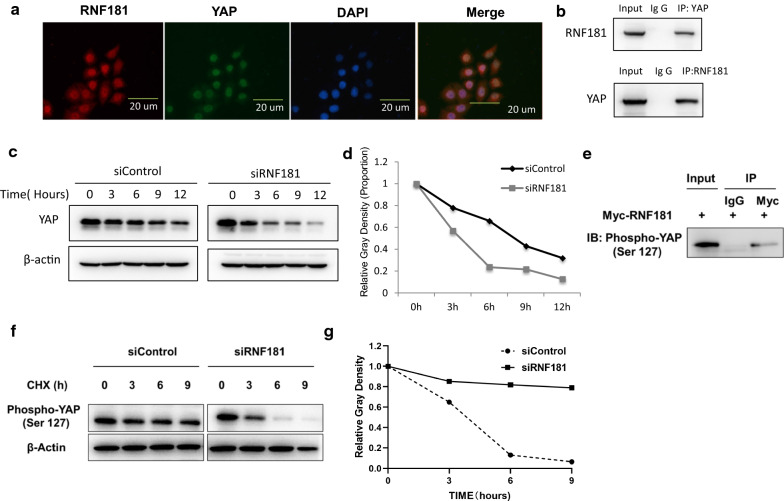
Fig. 5.
RNF181 facilitates YAP protein stability and inhibits YAP K48-linked poly-ubiquitination. a Intracellular localization analysis of RNF181 and YAP by immunofluorescence assay. BT549 cells were cultured in normal medium before fixation. Intracellular localization of YAP (red) and RNF181 (green) were shown. Nuclei (blue) were stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). b Co-IP assay revealed association between endogenous RNF181 and YAP protein in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells were harvested with RIPA lysis buffer. CO-IP was performed using antibody as indicated. c, d RNF181 consumption decreased YAP half-life in BT549 cells. BT549 cells were transfected with 50 µM siControl or siRNF181. After 24 h, cells were treated with 100 µM cycloheximide/vehicle for indicated times. Cell lysates were prepared for Western blot analysis. The results are representative for three independent experiments. The YAP relative density was measured by Image J software. e Co-IP assay revealed association between endogenous RNF181 and phospho-YAP (S127) protein in BT549 cells. BT549 cells were harvested with RIPA lysis buffer. CO-IP was performed using antibody as indicated. f, g RNF181 consumption decreased phospho-YAP (S127) half-life in BT549 cells. BT549 cells were transfected with 50 µM siControl or siRNF181. After 24 h, cells were treated with 100 µM cycloheximide/vehicle for indicated times. Cell lysates were prepared for Western blot analysis. The results are representative for three independent experiments. The phospho-YAP (S127) relative density was measured by Image J software