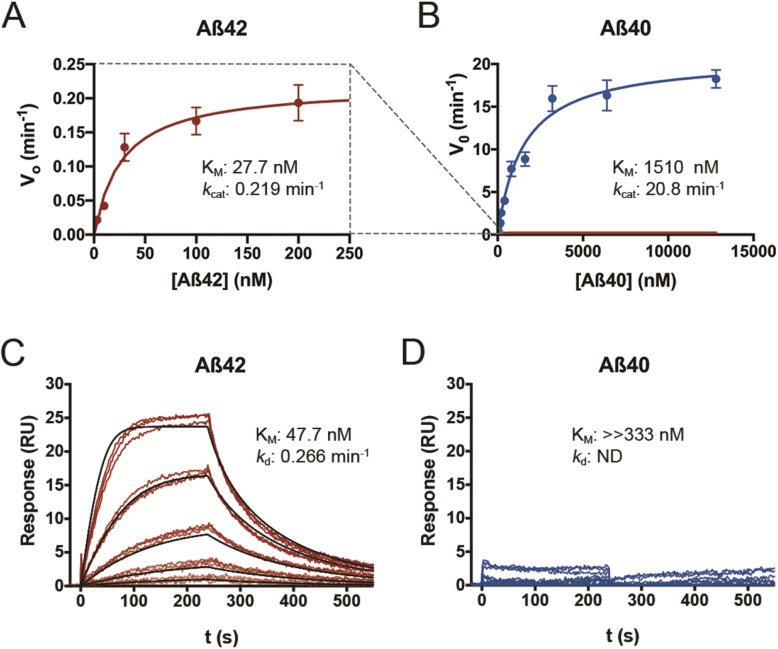
Fig. 3.
CatD degrades Aβ42 and Aβ40 with markedly different kinetics. a, b Plots of initial velocity (vo) vs. substrate concentration for Aβ42 (a, red) and Aβ40 (b, blue). The dashed lines (gray) show the relative position of the data in a when superimposed on the same scale as is used for the data in b. Quantitative kinetic parameters are provided in Supp. Table S2. c, d Surface plasmon resonance confirms that Aβ42 exhibits markedly higher affinity for CatD than Aβ40, independent of degradation. Traces obtained for 3-fold dilutions of Aβ42 (c) and Aβ40 (d) beginning at 333 nM. Analysis of the fitted curves in (c) yielded a KM of 47.7 + 0.041 nM and a kd value of 0.266 + 7.2 × 105 min−1 for Aβ42. Consistent with the kinetics of Aβ40 binding obtained by other methods (Supp. Table S2), no significant binding of Aβ40 was observed within the conditions used. Note that, for technical reasons, these experiments were conducted at pH 4.5, precluding direct quantitative comparisons to kinetic parameters determined by other methods at pH 4.0