FIGURE 2.
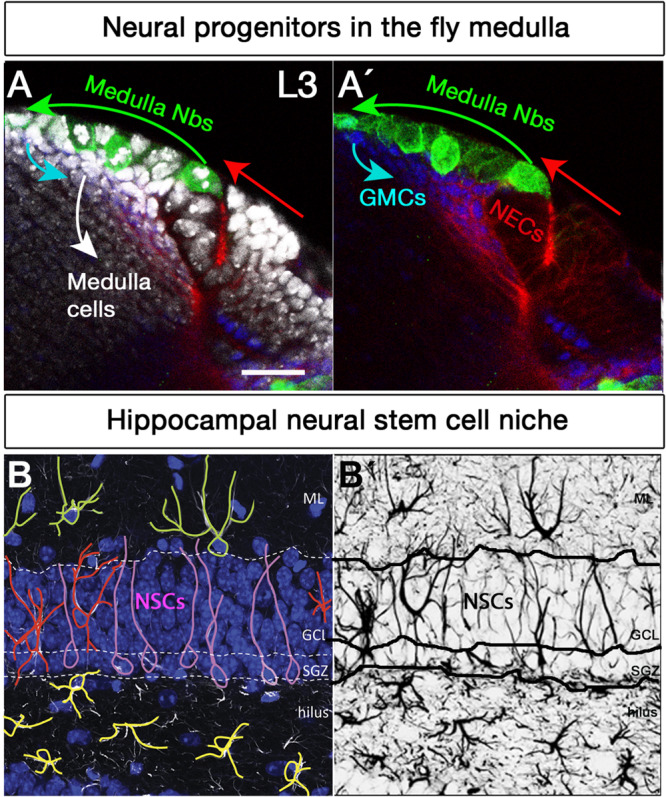
Neural stem cell niches in the Drosophila larval medulla and adult mouse hippocampus. (A,A’) Neural stem cell niche in the larval medulla: (A) neuroepithelial cells (NECs, DE-Cadherin, red) in the outer proliferation center, and their transition into medulla neuroblasts (Nbs, Miranda, green), ganglion mother cells (GMCs, Prospero, blue) and medulla postmitotic cells (DAPI, gray). Arrows indicate transition direction. Scale bar = 20 μm. (B,B’) Neural stem cell niche in the adult mouse hippocampus: (B) Neural stem cells with radial glia-like morphology (pink) are located in the hippocampal dentate gyrus (GFAP, white; DAPI, blue). Their soma sits at the border of the densely packed granule cell layer (GCL), the so-called subgranular zone (SGZ). Their primary process extends across the GCL and reaches the inner molecular layer (ML). NSCs express the markers Sox2, Prominin 1, Nestin (not shown) and glial fibrillary acidic protein GFAP (white), among others, and are mostly quiescent. Surrounding the NSCs a variety of highly branched niche astrocytes located in different layers are found. Those in the ML, GCL, and hilus are shown in green, red, and yellow, respectively. Mature astrocytes do not proliferate and express markers such as glial glutamate transporter 1 (GLT1), S100β (not shown) and GFAP (white), among others. Other niche elements such as blood vessels, INPs and neurons are not shown. (B’) GFAP immunostaining, marking both NSCs and astrocytes with distinctive morphologies.
