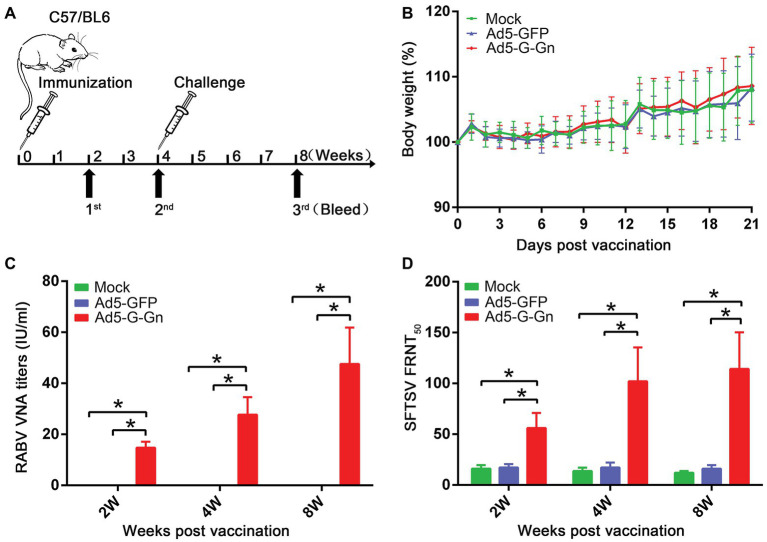
Figure 2.
Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of recombinant Ad5-G-Gn in mice. (A) The procedure of immunization, serum collection, and virus challenge in mice. C57/BL6 mice (male, 6–8 weeks old) were immunized intramuscularly (i.m.) with 108 GFU of Ad5-G-Gn, Ad5-GFP, or mock immunized with the same volume of Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM). Blood samples were collected at 2, 4, and 8 weeks after immunization. Viral challenge was carried out at 4 weeks after immunization. (B) Pathogenicity of Ad5-G-Gn in mice. Groups of C57/BL6 mice (6–8 week-old, male, n = 8) were immunized i.m. with 108 GFU of Ad5-G-Gn, Ad5-GFP, or the same volume of DMEM (Mock), and body weights were monitored daily for 21 days. Data from all mice in each group were measured as mean values ± SEM. (C,D). Groups of C57/BL6 mice (n = 24) were immunized with 108 GFU of Ad5-G-Gn, Ad5-GFP, or mock immunized with the same volume of DMEM by the i.m. route. At 2, 4, and 8 weeks post immunization, and blood samples were collected for virus-neutralizing antibody (VNA) test. Titers of rabies virus (RABV) neutralizing antibodies were examined by fluorescent antibody virus neutralization (FAVN) test (C). Titers of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) neutralizing antibodies were quantified for neutralization of SFTSV JS-2011-013-1 strain using an focus reduction neutralization test (FRNT) assay (D) (*p < 0.05).