Fig. 5 |. Topology of α-synuclein–membrane interactions.
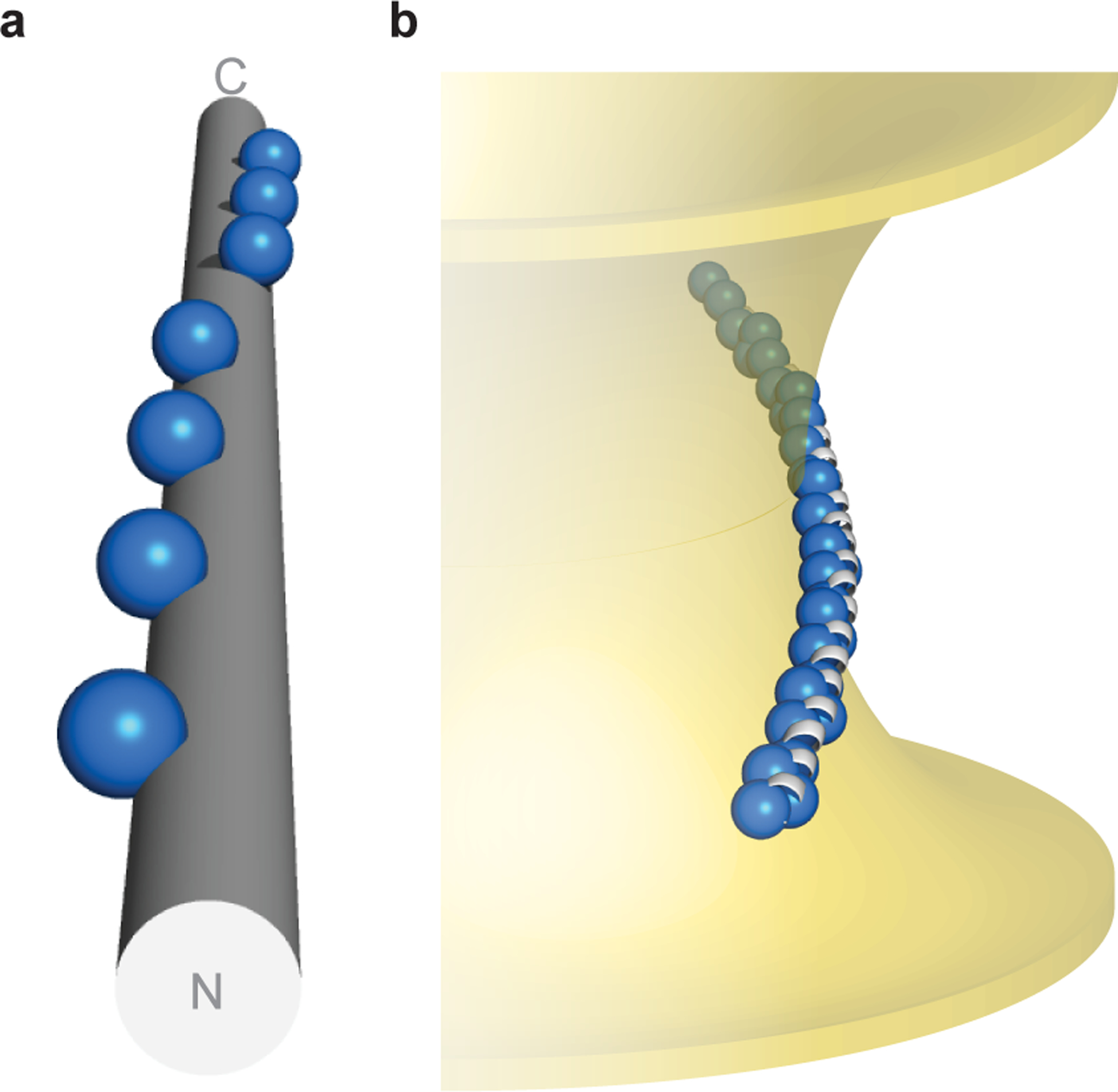
a, α-Synuclein’s hydrophobic residues (repeat position 2 shown as spheres) wind around an idealized α-helix ([φ, ψ] = [–57°, −47°], 3.60 residues/turn). b, Hypothetical model of α-synuclein interacting with membranes of negative Gaussian curvature, which is consistent with both NMR spectroscopy in the presence of anionic membranes of native-like composition16,39, as well as functional data in neurons45. Membrane-contacting residues (repeat positions 2, 6, 9, 10) shown as blue spheres.
