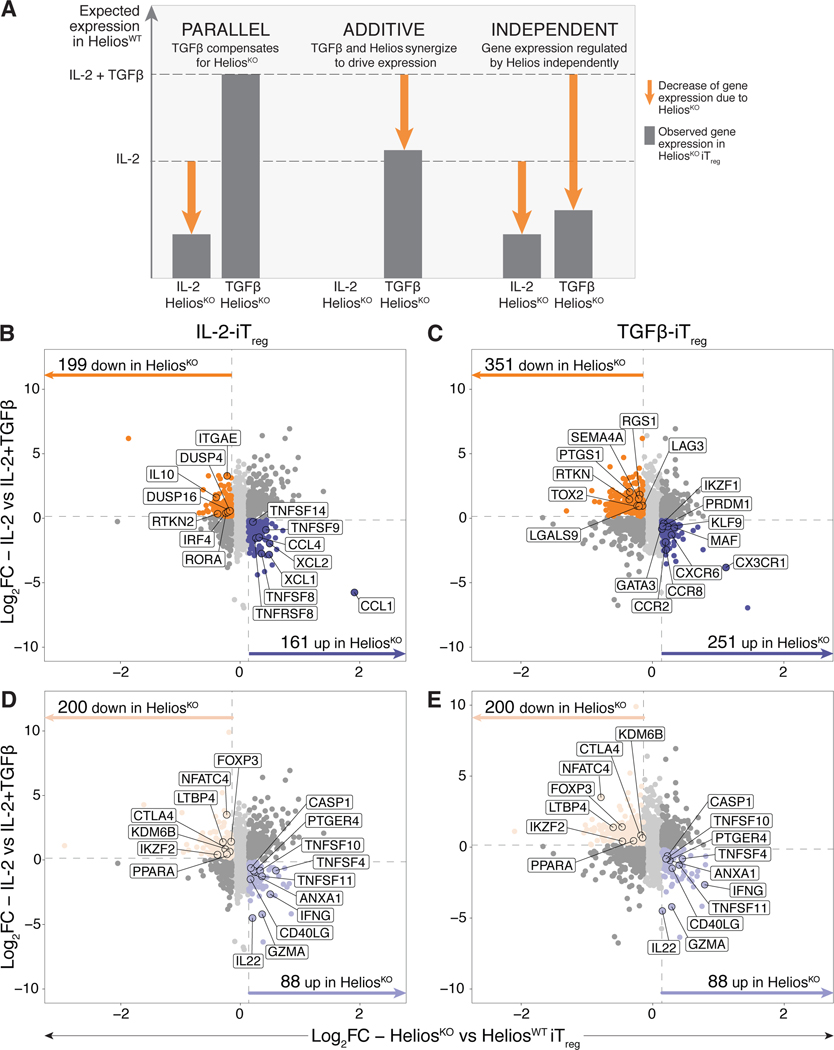
Figure 7. Ablation of Helios in fetal iTreg results in downregulation of Treg-specific genes, and the concurrent upregulation of pro-inflammatory genes.
CRISPR-Cas9 editing was carried out in fetal naïve T cells (n=6) with Helios gRNA1 (HeliosKO) or the non-targeting control guide (HeliosWT). Edited cells stimulated with αCD3/αCD28/αCD2 tetramers in the absence or presence of TGF-β for 6 days, after which changes in their overall transcriptome was assessed by RNAseq.
(A) Schematic showing hypothesized expression levels (dotted lines) of a Treg-specific gene that is upregulated with IL-2 in the absence or presence of TGF-β signaling, with proposed changes in transcription level given one of the three proposed scenarios of transcriptional control by Helios and TGF-β. Gene expression that is driven by Helios is shown, with the arrows denoting the corresponding decrease in gene expression occurring with Helios knockout.
(B, C) Scatterplots show log 2 fold change (log2FC) values comparing the absence or presence of exogenous TGFβ during the differentiation process (y-axis) and HeliosKO against HeliosWT iTreg (x-axis) that underwent differentiation in IL-2 alone (B) or with exogenous TGF-β added (C). Dotted lines in grey denote log2FC cut-offs. Only genes upregulated (dark purple) or downregulated (dark orange) in HeliosKO relative to HeliosWT iTreg cells are colored and shown (fold change, FC>1.1, false discovery rate, FDR<0.05). Genes associated with Treg or pro-inflammatory immune functions are outlined and labeled.
(D, E) Same scatterplots as in (B,C) for IL-2 only iTreg cells (D) and IL-2 + TGF-β-iTreg (E) now colored to only show shared genes meeting the same cutoffs that were upregulated (light purple) or downregulated (light orange) in HeliosKO relative to HeliosWT iTreg cells. Genes associated with Treg or pro-inflammatory immune functions within the shared Helios-regulated transcriptome are outlined and labeled.