Figure 1. IL-22 protects against OPC non-redundantly with IL-17RA.
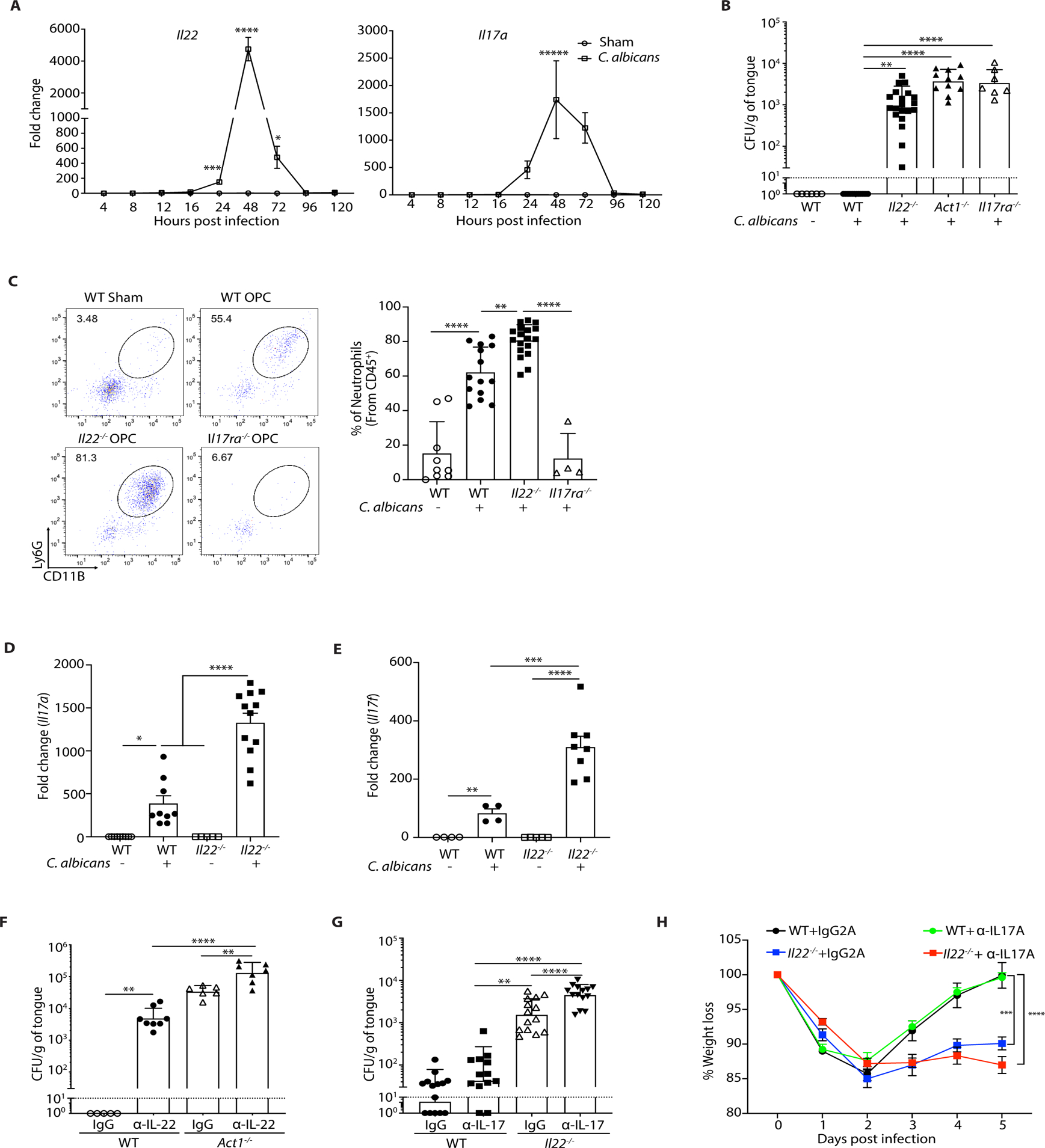
The indicated mice were sublingually inoculated with cotton ball-saturated PBS (Sham) or C. albicans (OPC). Each symbol represents one mouse. A. Total mRNA from tongue homogenates of infected WT mice was subjected to qPCR for Il22 and Il17a and normalized to Gapdh at each time point. Graphs show mean ± SEM. Data are pooled from 4–9 mice per group. B. Fungal burdens were determined by CFU enumeration on YPD/Amp agar at day 5 p.i. Graphs show geometric mean ± SD. Data were pooled from 3 independent experiments. Dashed line indicates limit of detection (~30 CFU/g). C. Tongue homogenates were prepared on day 2 p.i. Left: A representative FACS plot showing percent of CD11b+Ly6G+ neutrophils (gated on live, CD45+ cells). Right: Data from 3 independent experiments. D-E. Il17a and Il17f in total RNA from tongue on day 2 p.i. was assessed by qPCR relative to Gapdh. Graphs show mean ± SEM relative to Sham-infected WT mice. F. Mice were injected i.p. with anti-IL-22 or isotype control IgG (150 μg) on days −1, 0, 1, 2, and 3 relative to infection. CFU was assessed on day 4, pooled from 2 independent experiments. G. Mice were treated with anti-IL-17A or isotype control (IgG2a) (200 μg) injected i.p. on days −1, 1, and 3 relative to infection. CFU was assessed on day 5, pooled from 3 independent experiments. H. Weight loss was assessed daily, shown relative to day 0 in mice from panel F. Data were analyzed by ANOVA or Student’s t-test, with Mann-Whitney U test for fungal load analysis.
