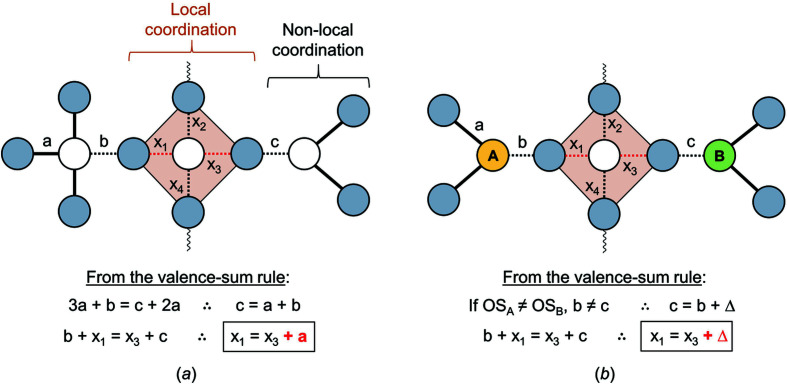
Figure 5.
Inherent bond-valence (and thus bond-length) variation resulting from the valence-sum rule for (a) different coordination numbers and (b) different oxidation states (OS) of next-nearest neighbours for a simple bond topology. Grey circles are anions. White circles are cations of the same oxidation state and coloured circles are cations of different oxidation states. The fragment shown is self-contained; wavy lines indicate further bonds which are inconsequential to x1 and x3. Black bonds are terminal and consequently equal to the oxidation state of the anion, ‘a’; from here, ‘b’ and ‘c’ are deduced, and x1 and x3 are shown to be necessarily unequal in strength, thus causing bond-length variation within the local coordination.