Take home figure .
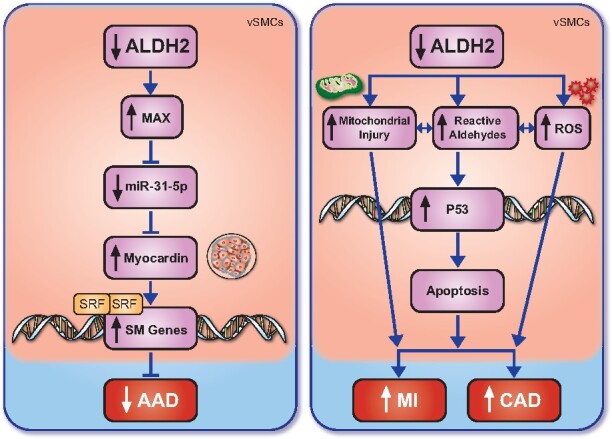
The role of ALDH2 in cardiovascular pathologies. ALDH2 mutation or inhibition reduces MAX levels and the expression of miR-31-5p, reducing myocardin production, thus inhibiting the production of contractile smooth muscle proteins and ultimately leading to the increased incidence of AAD. Conversely, a reduction in ALDH2 has been demonstrated to increase mitochondrial injury, reactive aldehyde production, and the presence of ROS, the latter two increasing p53 expression, leading to cellular apoptosis and ultimately an increase in myocardial infarction and coronary artery disease. AAD, aortic aneurysm/dissections; ALDH2, aldehyde dehydrogenase 2; CAD, coronary artery disease; MI, myocardial infarction; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SM Genes, smooth muscle cells; SRF, serum response factor .
