Fig. 2.
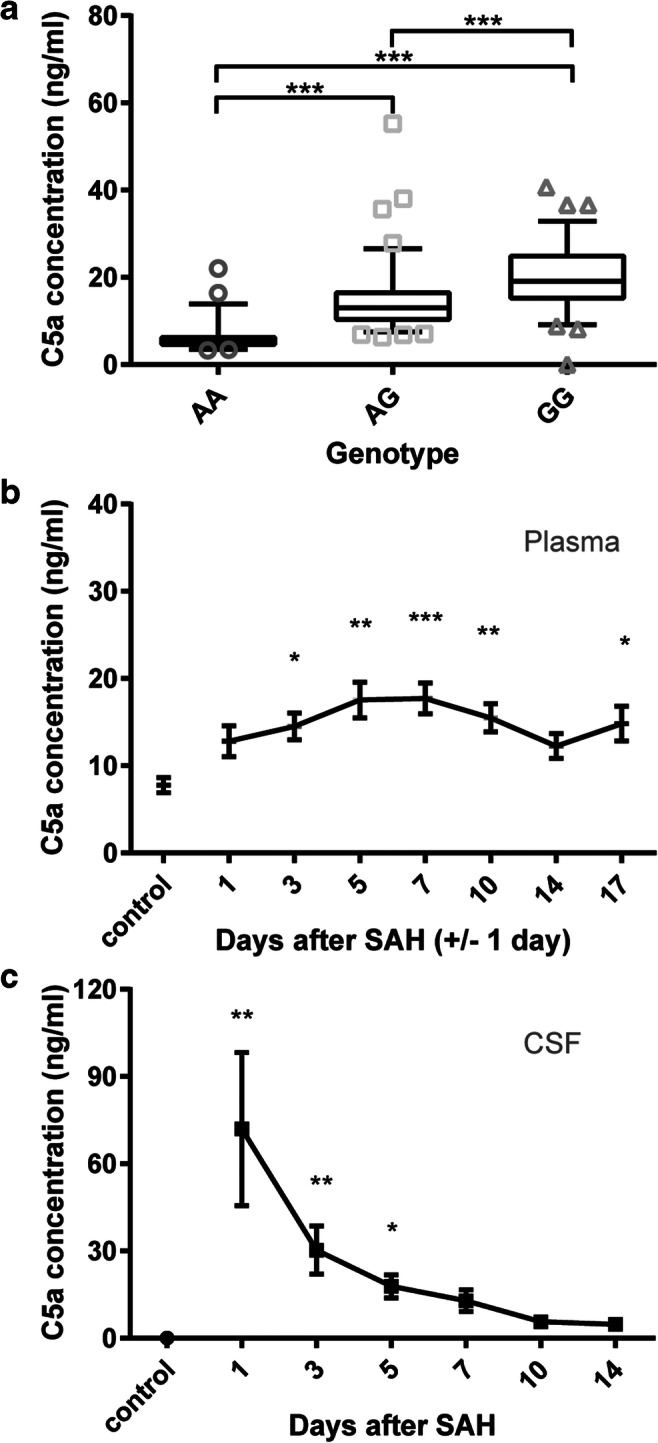
C5a levels measured in plasma and CSF of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients. a Plasma C5a levels (ng/mL) of genotyped patients, grouped per genotype of the C5 single nucleotide polymorphism rs17611; blood samples were obtained between day 1 and day 14 postsubarachnoid hemorrhage; AA; n = 53, AG; n = 98, GG; n = 78; Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn’s multiple comparison, ***p ≤ 0.001, median ± 5–95 percentile. b Sequentially measured C5a levels in plasma of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients (n = 31), versus plasma C5a levels of healthy controls (n = 17). Blood samples were taken on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14, and 17 (± 1 day) after subarachnoid hemorrhage. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc; mean ± SEM. c Sequentially measured C5a levels in CSF of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients (n = 10) versus CSF C5a levels of patients with an unruptured aneurysm (n = 3). CSF obtained on days 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 12, and 14 after subarachnoid hemorrhage. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, Kruskal-Wallis test, Dunn’s post hoc; mean ± SEM
