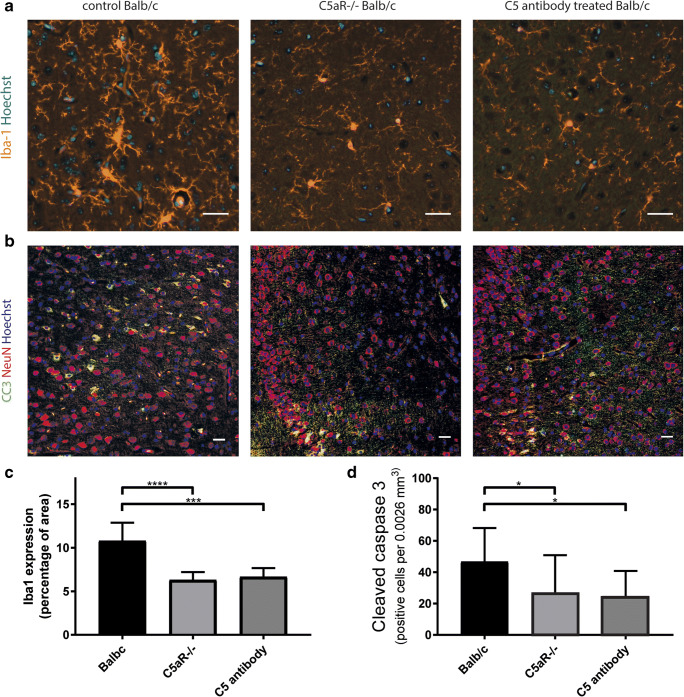
Fig. 3.
C5 antibody treatment reduces brain injury in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. a Representative images of mouse cortex stained with antibody against Iba-1 (orange); cell nuclei in blue (Hoechst). b Representative images of mouse cortex stained with antibody against cleaved caspase 3 (CC3; green); NeuN (red) and cell nuclei in blue (Hoechst). c C5a receptor deficient (C5aR−/−) and wild-type mice treated with C5-specific antibodies had a > 38% reduction in microglia/macrophage activation compared to untreated wild-type mice. Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn’s post hoc. d C5aR−/− mice and control BALB/c mice treated with C5-specific monoclonal antibodies had > 39% reduction in cells undergoing apoptosis, compared to untreated wild-type mice 48 h after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn’s post hoc; n = 15 mice per group; ****p ≤ 0.0001, ***p ≤ 0.001, *p ≤ 0.05; mean ± SD; scale bars 30 μm.