Fig. 4.
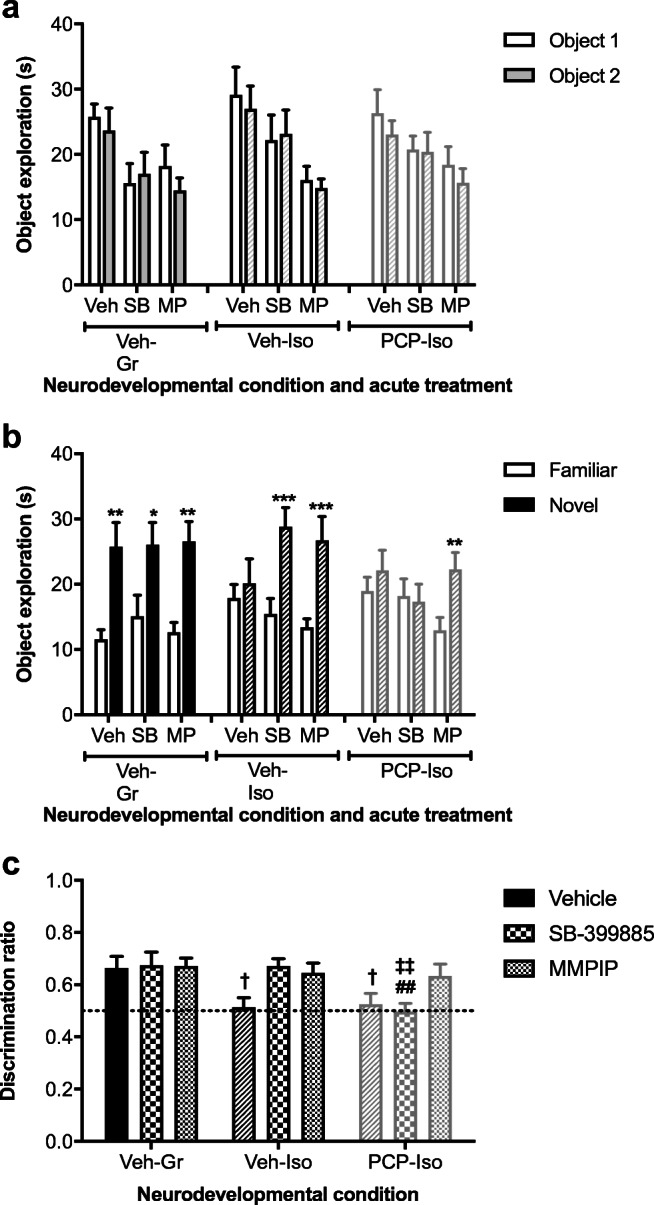
Impact of combined neonatal PCP and isolation rearing on the ability of a 5-HT6 (but not mGlu7) antagonist to reverse isolation-induced cognitive deficits in the NOD task. Mean ± SEM time spent exploring a two identical objects during the familiarization trial and b the novel and familiar object during the choice trial 2 h later, as well as c choice trial discrimination ratio (time exploring novel/total choice trial object exploration). Male Lister hooded rats that received saline (1 ml/kg s.c.; Veh) or PCP (10 mg/kg) on PND 7, 9, and 11 were housed in groups (Gr; Veh only) or isolation (Iso; Veh and PCP) from weaning on PND 21, then underwent NOD on three occasions at 1–2-week intervals (PND 57–80) to receive acute vehicle (Veh; 0.5% methylcellulose 1% Tween 80; 1 ml/kg i.p. 30 min before the familiarization trial), SB-399885 (SB; 10 mg/kg), or MMPIP (MP; 10 mg/kg) on separate test days in a pseudorandom order and serve as their own controls (n = 13–14 per neurodevelopmental condition). In the familiarization trial a, there was a main effect of acute treatment on the duration of object exploration (P < 0.001), which was decreased by SB-399885 and MMPIP, but importantly, no spatial preference between identical objects or any neurodevelopmental condition × treatment interaction. In the choice trial b, there was an effect of object (P < 0.001) and an object × neurodevelopmental condition interaction (P < 0.01). Veh-Gr discriminated the novel object following acute vehicle and this intact memory was not further enhanced by acute treatment, consistent with a ceiling effect. Impaired memory was restored by SB-399885 in single-hit Veh-Iso but not dual-hit PCP-Iso, whereas MMPIP remained effective in both models. Accordingly, discrimination ratios (c) were lower in Veh-Iso and PCP-Iso than in Veh-Gr following acute vehicle, and of note also lower in PCP-Iso than the other two neurodevelopmental conditions following acute SB-399885. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus the familiar object following the same acute treatment in the same rats (three-way repeated measures ANOVA with Sidak post hoc); †P < 0.05 versus acute vehicle in Veh-Gr, ‡‡P < 0.01 versus acute SB-399885 in Veh-Gr; ##P < 0.01 versus acute SB-399885 in Veh-Iso (two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc)
