Fig. 7.
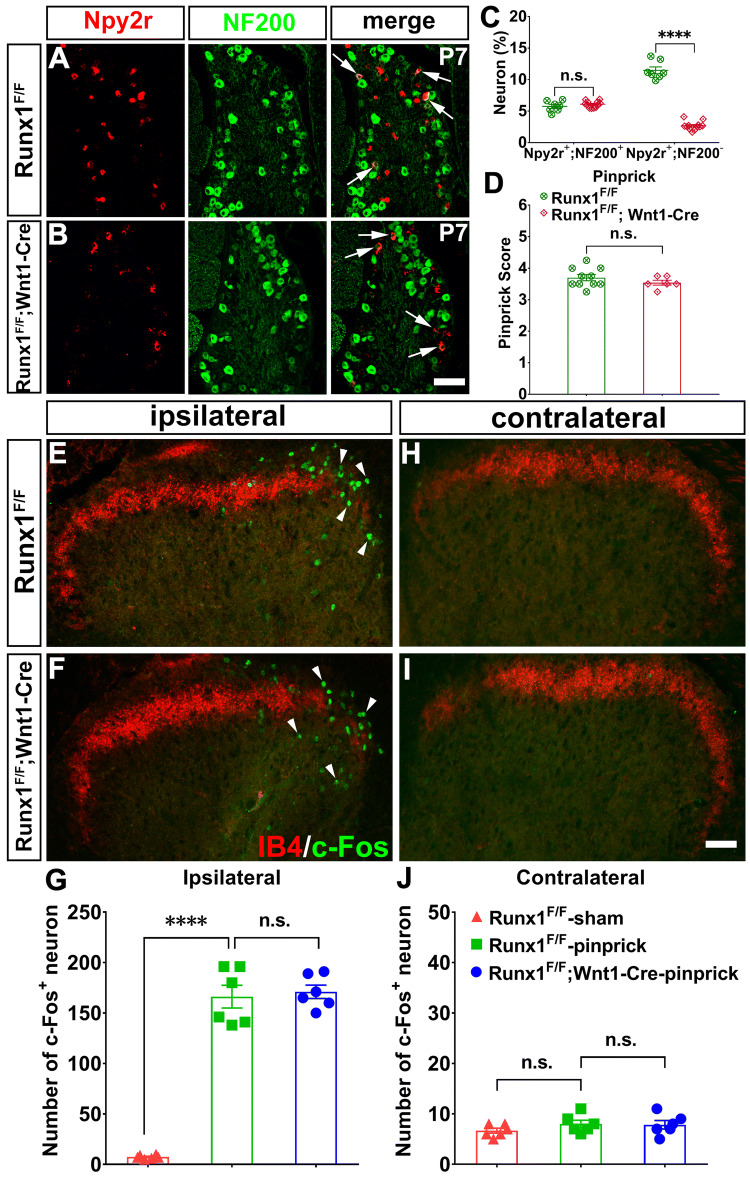
Requirement of Runx1 for the development of Npy2r-persistent but not Npy2r-transient neurons. A, B Representative images of ISH with the Npy2r probe plus NF200 immunostaining in sections through lumbar DRGs from P7 Runx1F/F control and Runx1F/F;Wnt1-Cre mutant mice (arrows, Npy2r+;NF200+ neurons; scale bar, 100 µm). C Percentages of Npy2r+;NF200+ and Npy2r+;NF200− among all neurons in Runx1F/F control and Runx1F/F;Wnt1-Cre CKO mice. D Pinprick scores evoked by a sharp steel pin glued to the tip of 1.0 g von Frey filament in Runx1F/F control (n = 10) and Runx1F/F;Wnt1-Cre mice (n = 6) (Student’s unpaired t-test, P = 0.2766, t(14) = 1.132). E, F Pinprick-evoked c-Fos expression in the ipsilateral dorsal horns in Runx1F/F control and Runx1F/F;Wnt1-Cre CKO mice. G Statistical comparison of c-Fos+ neuronal numbers in the ipsilateral dorsal horns between Runx1F/F control and Runx1F/F;Wnt1-Cre CKO mice (n = 6/group, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc analysis, F2, 15 =151.7, ****P < 0.0001). H, I C-Fos in the contralateral dorsal horn in Runx1F/F control and Runx1F/F;Wnt1-Cre CKO mice. J Statistical comparison of c-Fos+ neuronal numbers in the contralateral dorsal horn between Runx1F/F control and Runx1F/F;Wnt1-Cre CKO mice (n = 6/group, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc analysis, F2, 15 =1.075, P = 0.366).