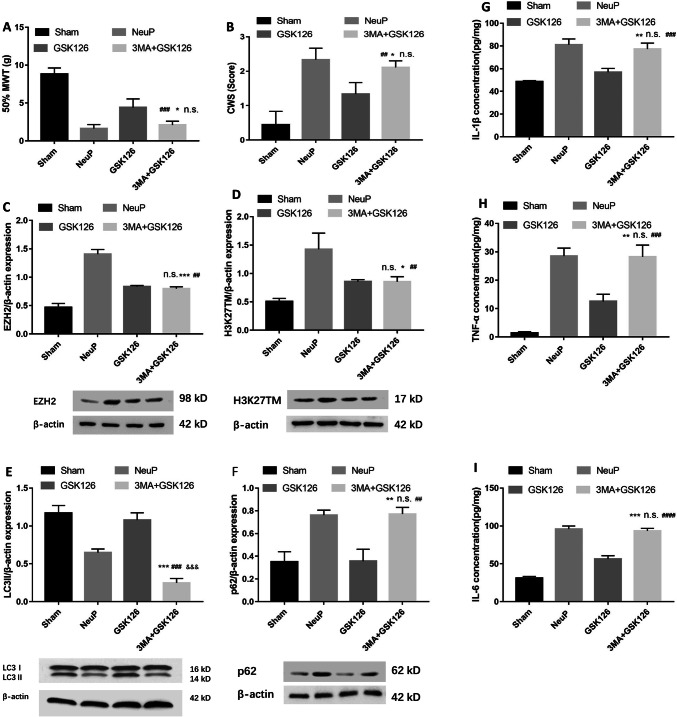
Fig. 6.
Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA impairs EZH2 inhibitor-induced pain relief and neuroinflammation remission. A, B Mechanical allodynia (A) and cold allodynia (B) in sham-operated and neuropathic pain groups after 3-MA combined with GSK126 treatment from day 1 to day 3 post-surgery (mean ± SD; n = 8; n.s., no significant difference vs NeuP group; *P < 0.05 vs GSK126 group; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs Sham group). C–F Relative expression of EZH2 (C) and H3K27TM (D) (mean ± SD; n = 8; n.s., no significant difference vs GSK126 group; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs NeuP group; ##P < 0.01 vs Sham group), LC3II (E) (mean ± SD; n = 8; ***P < 0.001 vs NeuP group; ###P < 0.001 vs GSK126 group; &&&P < 0.001 vs Sham group), and p62 protein (F) (mean ± SD; n = 8; **P < 0.01 vs GSK126 group; n.s., no significant difference vs NeuP group; ##P < 0.01 vs Sham group) in the ACC of rats after 3-MA combined with GSK126 treatment from day 1 to day 3 post-surgery. G–I ELISA analysis of IL-1β (G), TNF-α (H), and IL-6 (I) expression levels in the ACC of the Sham and NeuP groups after 3-MA combined with GSK126 treatment from day 1 to day 3 post-surgery (mean ± SD; n = 8; n.s., no significant difference vs NeuP group; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs GSK126 group; ###P < 0.001, ####P < 0.0001 vs Sham group).