Figure 3.
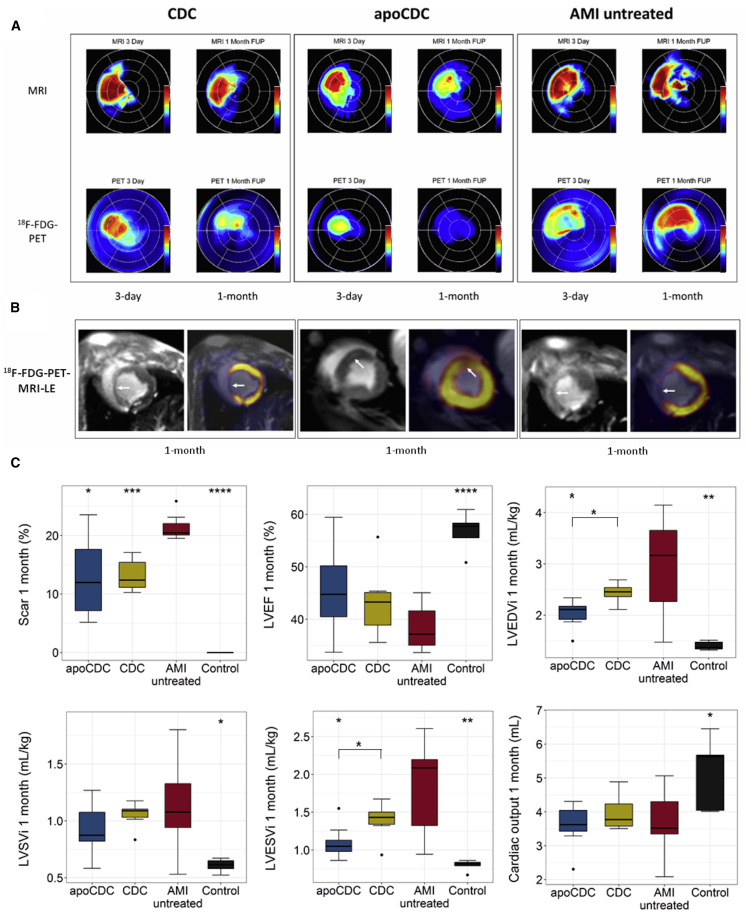
Representative [18F]FDG-PET-MRI Polar Map Imaging with Late Enhancement of Porcine Hearts after AMI and Treatment with apoCDCs, CDCs, or Saline (AMI Untreated) at 3 Days and 1 Month and Summary of Functional Parameters Detected by PET-MRI Imaging
(A) At 3 days, similar-sized transmurality (red color) was detected in all 3 groups, with decreasing transmurality in CDC and apoCDC groups at the 1-month follow-up period (FUP). Reduced viability was found in the anteroseptal region with visual smaller size of nonviable and reduced viable areas both at 3 days and 1 month FUP in the apoCDC group. (B) MRI and MRI-PET fusion images. Group CDC (left): MRI showed myocardial thinning and increased signal intensity in the mid-anteroseptal/apical anterior segments. MRI-PET fusion image indicated reduced tracer uptake in the same region (arrows). Group apoCDC (middle): MRI showed high late-enhancement signal intensity in the apical septal segment, and MRI-PET fusion image demonstrated tracer uptake in the same region (arrows). Group AMI untreated (right): a large infarct resulted in myocardial thinning and delayed enhancement in the mid-anteroseptal and apical segments (arrows). MRI and PET image fusion was done for visualization purposes in 3D Slicer software. (C) Scar area, LV EF, end-diastolic (LV EDV index [LVEDVi]), stroke volume (LV SV index [LVSVi]), and end-systolic (LV ESV index [LVESVi]) indices relative to body weight and cardiac output were assessed by cardiac MRI, 1 month after infarction and cell treatment. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc) compared to AMI untreated (scar, LVESV, LVEDV) or between apoCDC and CDC where indicated.