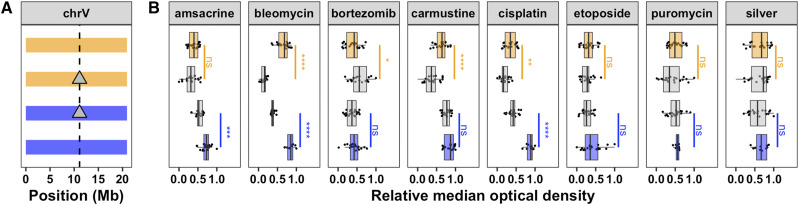
Figure 5.
Testing the role of scb-1 in drug responses. (A) Strain genotypes on chromosome V are shown, colored orange (N2) and blue (CB4856). From top to bottom, strains are N2, ECA1132, ECA1134, and CB4856. Deletion of scb-1 is indicated by a gray triangle. The dotted vertical line represents the location of scb-1. (B) Phenotypes of strains in eight chemotherapeutics (12.5 µM amsacrine, 12.5 µM bleomycin, 2 µM bortezomib, 250 µM carmustine, 125 µM cisplatin, 62.5 µM etoposide, 300 µM puromycin, and 100 µM silver) are plotted as Tukey box plots with strain (y-axis) by relative median optical density (median.EXT, x-axis). Statistical significance was calculated for each strain pair (File S7). Significance of each deletion strain compared to its parental strain (ECA1132 to N2 and ECA1134 to CB4856) is shown above each strain pair and colored by the parent strain against which it was tested (ns = non-significant (p-value > 0.05); *, **, ***, and **** = significant (p-value < 0.05, 0.01, 0.001, or 0.0001, respectively).