Figure 2 -.
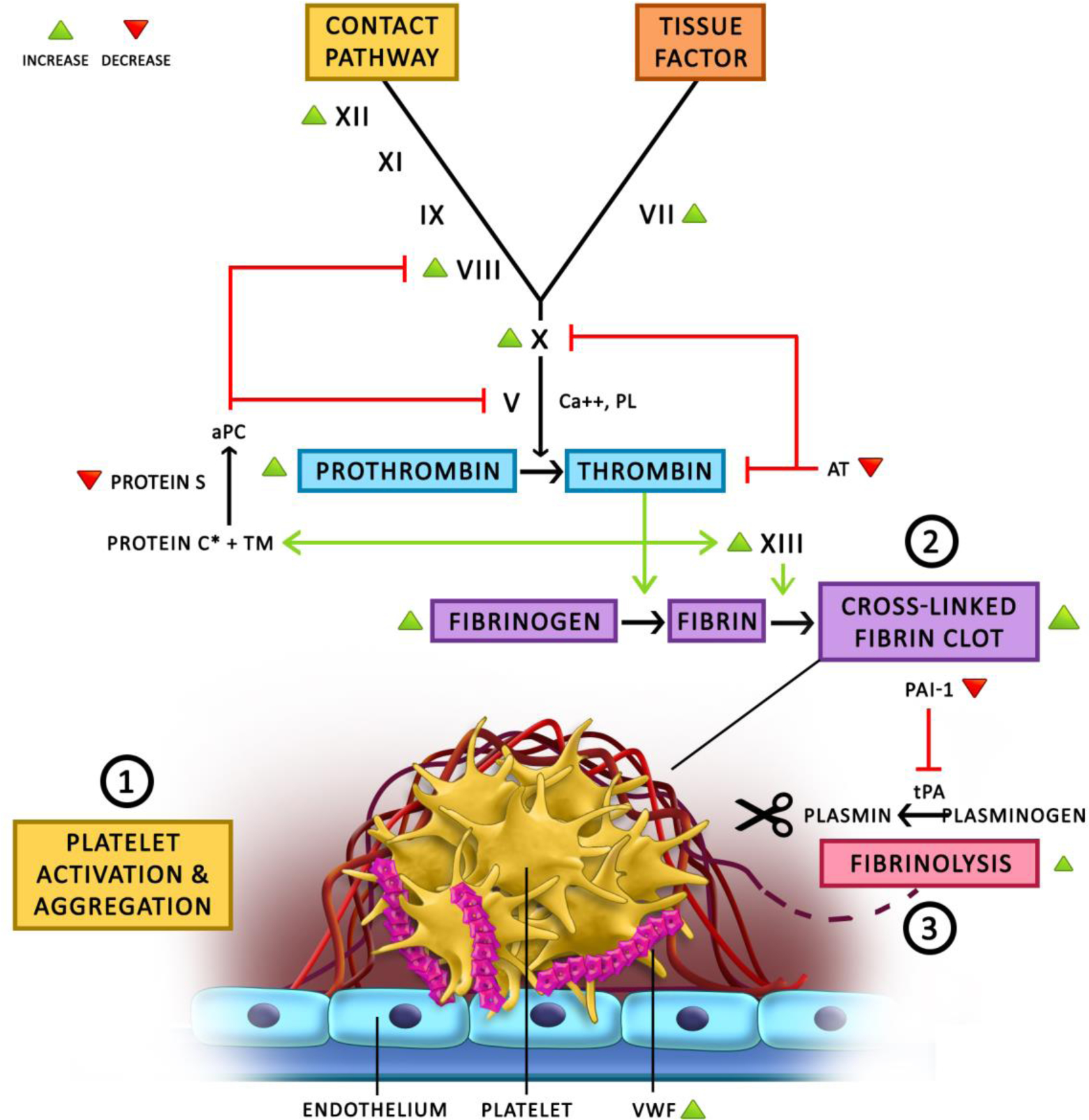
This diagram demonstrates our current understanding of the effects of estrogen on hemostasis & thrombosis. 1) The exact effect of estrogen on platelet activation and aggregation remains unclear, with conflicting reports in the literature showing altered platelet behavior. Estrogen is known to increase VWF levels which plays a central role in platelet adhesion and activation. 2) Estrogen leads to increased thrombin generation and fibrin clot formation by increasing the levels of variable coagulation proteins (green arrowheads) and decreasing the levels of anticoagulant proteins (red arrowheads). 3) Conversely, estrogen has also been shown to be associated with increased fibrinolysis due to decreased PAI-1 levels, which does not seem to balance out the increase in coagulation. Thus the net effect overall, has been shown to be prothrombotic.
aPC = activated Protein C
AT = anti-thrombin
PAI-1 = plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
PL = phospholipid
TM = thrombomodulin
tPA = tissue plasminogen activator
VWF = von Willebrand Factor
* In different studies, estrogen has been shown to increase Protein C antigen levels but also increase Protein C resistance
