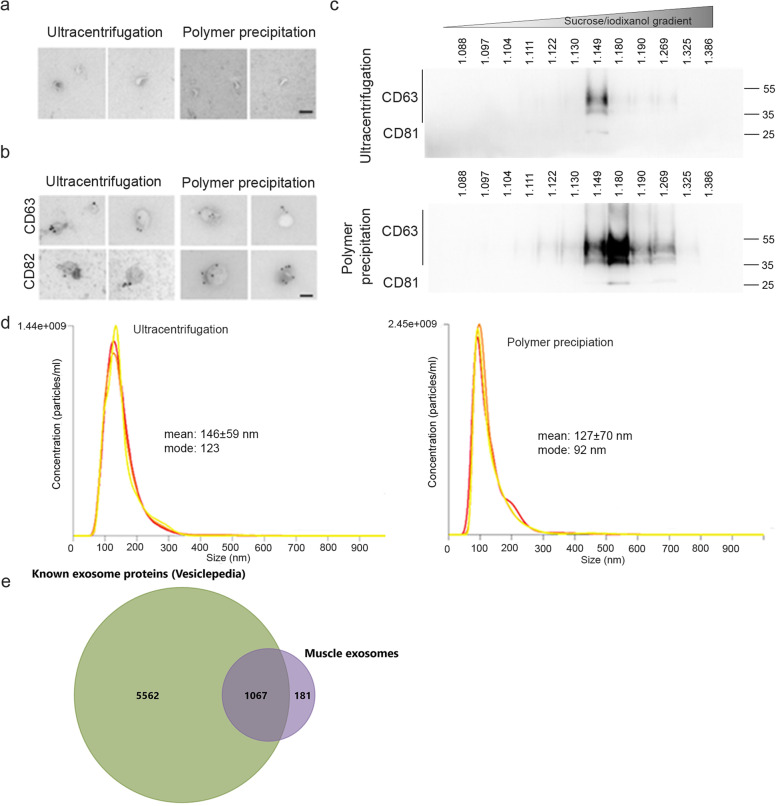
Fig. 4.
Validation of exosome extraction strategy. For each experiment, exosomes were extracted from the culture medium of 100 × 106 myoblasts differentiated into myotubes for 3 days using either the ultracentrifugation or the polymer precipitation. The culture medium was non-supplemented DMEM (without serum). a Cup-shaped vesicles were observed by electron microscopy with both extraction protocols. bar = 100 nm. b Both extractions show vesicles that are positive for CD63 and CD82 by electron microscopy. Bar = 100 nm. c Exosome extracts were loaded on iodixanol gradients as described in material and methods. Western blot results are shown for CD63 and CD81 in twelve fractions for the iodixanol gradient. Top panel: exosomes extracted by ultracentrifugation. Bottom panel: exosomes extracted by polymer-based precipitation. Exosomes were detected at a density of 1.15–1.27 g.ml−1. d Nanosight analyses show similar-sized vesicles using both strategies, from 100–200 nm, with a greater number of particles being detected when using the polymer extraction. e Proteomic analysis of muscle exosomes. Venn diagram showing the overlap between muscle exosomes and proteins known to be detected by mass spectrometry in exosomes (Vesiclepedia, Exocarta database [36–39])