Figure 1.
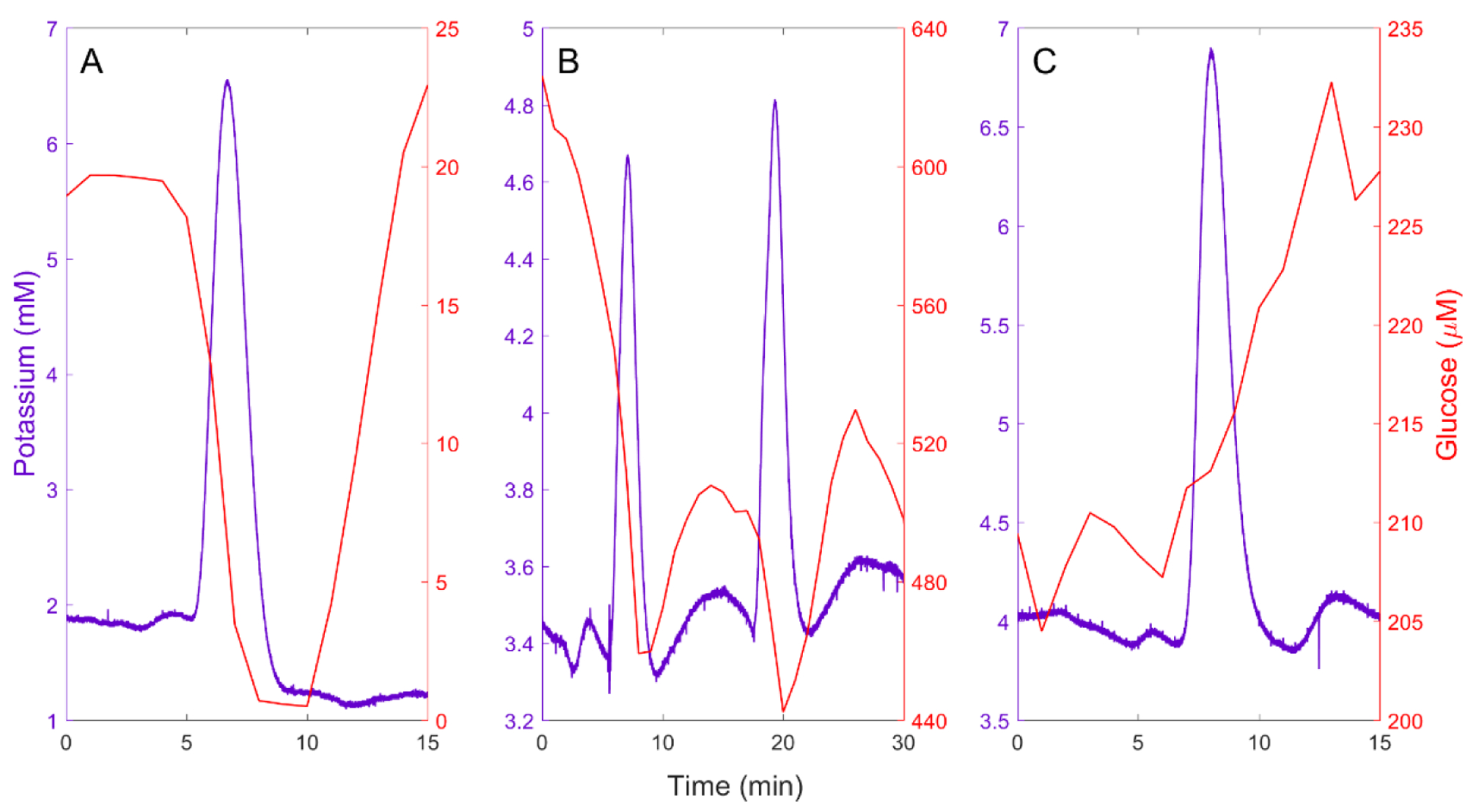
A) An isolated spontaneous SD accompanied by a negative glucose transient. B) A cluster of two closely spaced spontaneous SDs: the second SD triggers a negative glucose transient before the complete recovery of the prior negative glucose transient. C) A spontaneous SD accompanied by an increase in glucose, possibly indicating a change in blood flow.
