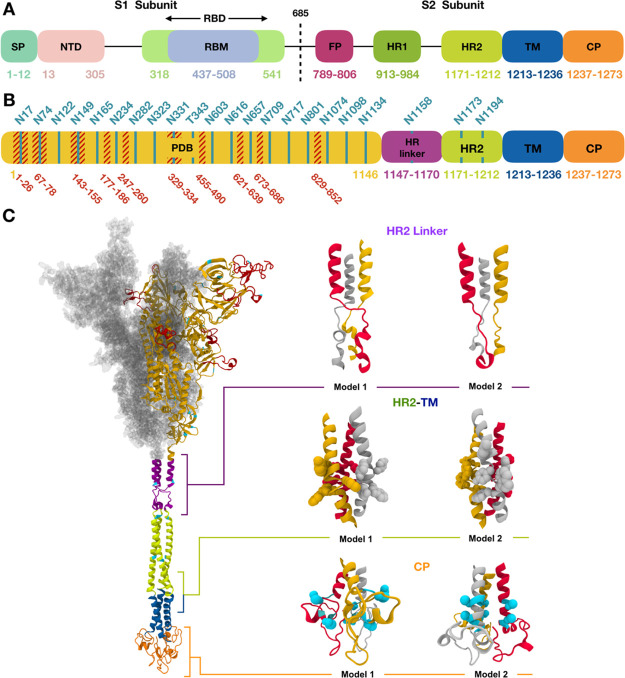
Figure 1.
(A) Assignment of functional domains in SARS-CoV-2 S protein: SP, NTD, RBD, receptor binding motif, FP, HR1, HR2, TM, and CP. (B) Assignment of modeling units used for model building. Glycosylation sites are indicated by residue numbers at the top. Missing loops longer than 10 residues or including a glycosylation site in PDB: 6VSB chain A are highlighted in red. Modeled glycosylation sites are shown in cyan. (C) A model structure of full-length SARS-CoV-2 S protein is shown on the left panel using the domain-wise coloring scheme in (B). For the PDB region, only one chain is represented by a secondary structure, while the other chains are represented by the surface. Two models selected for each HR linker, HR2-TM, and CP domain are enlarged on the right panel of (C). Trp and Tyr in HR2-TM are shown in spheres, which are key residues placed on a plane to form interactions with the lipid head group. For CP domain models, the Cys cluster is known to have high probabilities of palmitoylation. Cys1236 and Cys1241 for model 1 and Cys1236 and Cys1240 for model 2 are selected for palmitoylation sites in this study and are represented as cyan spheres. Illustration of S proteins was generated using VMD.14