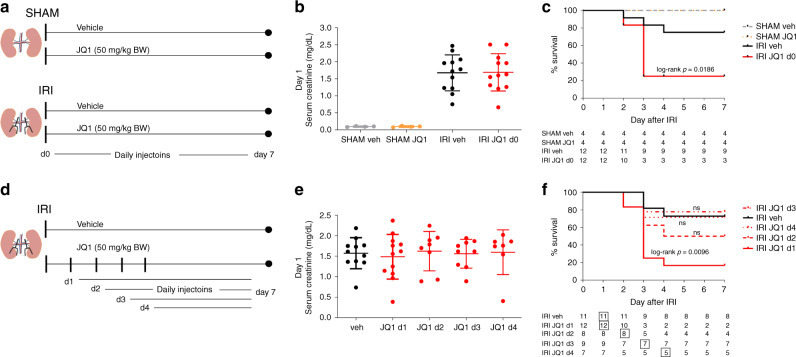
Fig. 5. Phenotypic consequences of BET inhibition after experimental AKI.
a C57BL/6N mice (10- to 12-week-old males) were treated daily starting at the day of SHAM or IRI surgery (d0) with JQ1 (50 mg/kg BW) or vehicle (DMSO/10% ß-cyclo dextrin 1:10). b Serum creatinine (mg/dL) values in SHAM and IRI animals with vehicle or JQ1 at day 1 after surgery are shown (individual data points and mean ± SD). SHAM: n = 4; IRI: n = 12 biologically independent samples. c Survival curves after IRI surgery (ischemic time was 26 min at 37 °C). JQ1 treatment leads to 80% mortality after IRI surgery. Table shows number of animals alive at indicated days. d Experimental design of delayed treatment with JQ1 (50 mg/kg BW) after IRI starting at day 1, day 2, day 3 or day 4. e Serum creatinine levels at day 1 after IRI, verifying that AKI was induced to a roughly equivalent extent in each of the groups of animals that were subsequently treated with JQ1 (individual data points and mean ± SD). IRI veh: n = 11; IRI d1: n = 12; IRI d2: n = 8; IRI d3: n = 9; IRI d4: n = 7 biologically independent samples. f Survival curve after delayed JQ1 treatment starting day 1, day 2, day 3 or day 4. Table indicates number of animals alive at each day. Box indicates start of vehicle or JQ1 treatment. Source data are provided as a Source data file.