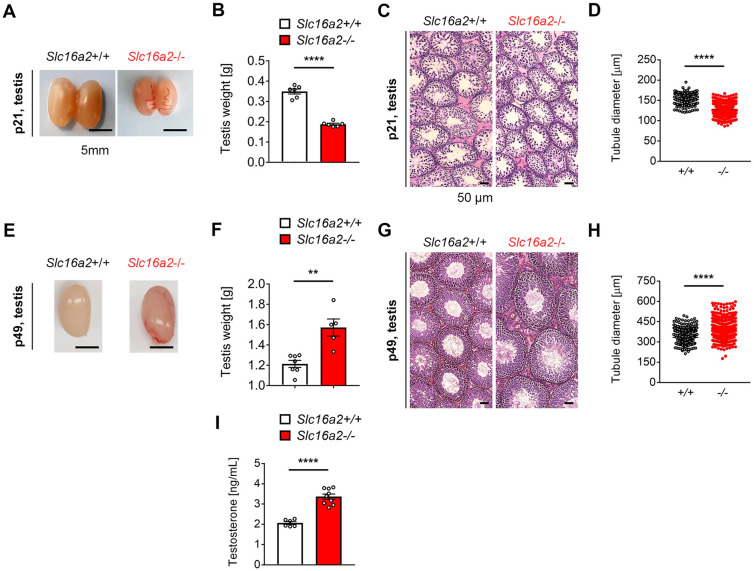
Figure 4.
Altered testis development of Slc16a2−/− rat. (A) Representative images of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p21. (B) Testis weights of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p21. n = 6 for each genotypes. (C) Representative images of H&E stained sections of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p21. (D) Diameter of seminiferous tubules of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p21 n = 4 for each genotypes. (E) Representative image of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p49. (F) Testis weights of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p49. n = 7 for Slc16a2+/+ and n = 5 for Slc16a2−/−. (G) Representative images of H&E stained testis sections of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p49. (H) Diameter of seminiferous tubules of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− rats at p49. n = 4 for each genotypes. (I) Serum testosterone levels of Slc16a2+/+ and Slc16a2−/− male rats at p49. n = 6 for Slc16a2+/+ and n = 9 for Slc16a2−/−, P < 0.01;**, P < 0.001;*** P < 0.0001;****.