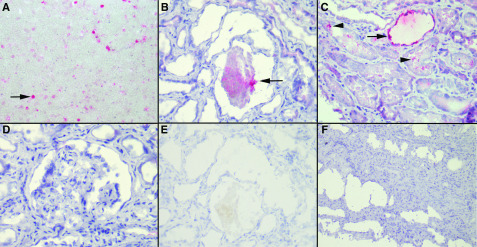
Figure 2.
Immunohistochemistry with an mAb against Plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein-2 revealed the presence of the parasite antigen in the lumina of the tubules. (A) P. falciparum–infected red blood cells as a positive control (arrow; ×400). (B) P. falciparum parasites in the tubule lumen (arrow; ×400). (C) P. falciparum parasites in the tubule lumen (arrowheads) and cytoplasm (arrow; ×400). (D) Absence of parasites in FSGS lesions (×400). (E) Negative control, with omission of the primary antibody (×400), for comparison with (B). (F) Absence of staining in a negative control consisting of a patient with HIV-associated nephropathy without malaria (×200). Similar results were obtained for patients with acute tubular necrosis unrelated to malaria.