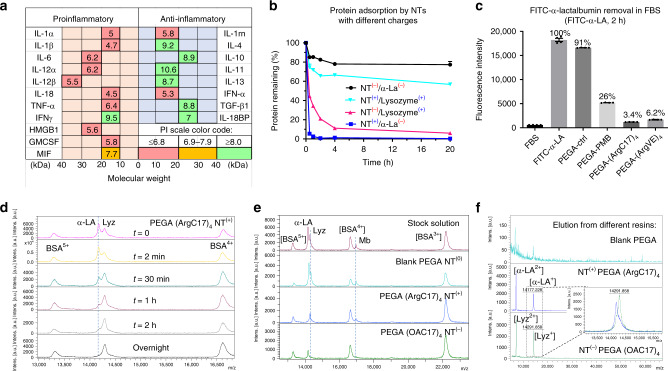
Fig. 4. Selective protein adsorption in TD NT resins based on charge interactions.
a Summary of the molecular weights and isoelectric points (PIs) of key proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in human sepsis. b The kinetic adsorption profiles of FITC-labeled α-LA(−) and lysozyme(+) by nanotrap (NT) resins with positive (arginine) or negative (oxalic acid (OA)) charges, respectively. NT(+): PEGA-(ArgC17)4; NT(−): PEGA-(OAC17)4 (n = 2, mean ± SD). c The adsorption efficiency of negatively charged FITC-labeled α-lactalbumin (α-LA, 14.2 kDa, PI: 4.5) by various positively charged resins in FBS after 2-h incubation (n = 4, mean ± SEM). d MALDI-TOF MS analysis of the protein mixture solution of α-LA (14.2 kDa, PI: 4.5, 0.5 mg per mL), lysozyme (Lyz, 14.4 kDa, PI: 10.7, 0.5 mg/mL), and BSA (66 kDa, PI: 4.2, 5 mg/mL) before and after incubation with NT(+) PEGA-(ArgC17)4 resin for different time at a bead/solution ratio of 1:10 v/v. Selective α-LA adsorption was observed. e MALDI-TOF MS analysis of the protein mixture solution of α-LA(−) (0.1 mg per mL), lysozyme(+) (Lyz, 0.1 mg per mL), myoglobin(0) (Mb, 0.1 mg per mL, PI: 7.1, 16.7 kDa), and BSA(−) (1 mg per mL, PI: 4.8–5.4, 66.4 kDa) before and after incubation with blank-acetylated PEGA, positive NT(+) PEGA-(ArgC17)4, and negative NT(−) PEGA-(OAC17)4 resins, respectively, at bead/solution ratio of 1:4 v/v. Charge-specific protein adsorption was observed. f MALDI-TOF MS analysis of proteins eluted from nanotrap resins after protein adsorption with 8 M urea: weak signals were observed from blank resin eluent, and strong signal and charge selectivity were observed for charged TD resins. Source data are available in the Source Data file.