Figure 4.
Brd9 Deletion Reduces Foxp3 Binding at CNS0 and CNS2 Enhancers and a Subset of Foxp3 Target Sites
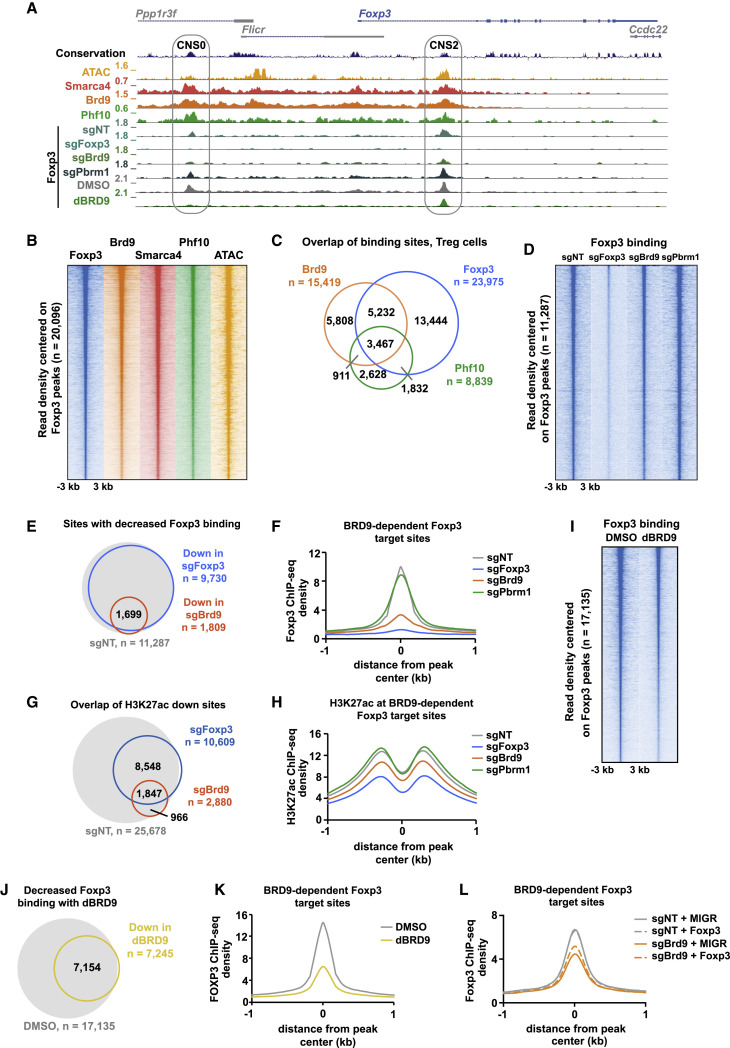
(A) Genome browser tracks of Smarca4, Brd9, and Phf10 ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq signals as well as Foxp3 ChIP-seq in sgNT, sgFoxp3, sgBrd9, and sgPbrm1 Treg cells and Foxp3 in DMSO- and dBRD9-treated Treg cells (2.5 μM dBRD9 for 4 days). The Foxp3 locus is shown with CNS0 and CNS2 enhancers, indicated as gray ovals.
(B) Heatmap of Foxp3, Brd9, Smarca4, and Phf10 ChIP-seq and ATAC-seq signals ± 3 kb, centered on Foxp3-bound sites in Treg, ranked according to Foxp3 read density.
(C) Venn diagram of the overlap between ChIP-seq peaks in Treg cells for Brd9, Foxp3, and Phf10 (hypergeometric p of Brd9:Foxp3 overlap = e−27665, hypergeometric p of PHF10:Foxp3 overlap = e−17185, hypergeometric p of Brd9:PHF10 overlap = e−14217).
(D) Heatmap of Foxp3 ChIP-seq signals in sgNT, sgFoxp3, sgBrd9, and sgPbrm1 Treg cells ± 3 kb, centered on Foxp3-bound sites in sgNT, ranked according to read density.
(E) Venn diagram of the overlap (hypergeometric p = e−11,653) between sites that significantly lose Foxp3 binding (FC 1.5, Poisson p < 0.0001) in sgFoxp3 and sgBrd9, overlaid on all Foxp3-bound sites in sgNT (gray).
(F) Histogram of Foxp3 ChIP read density ± 1 kb surrounding the peak center of sites that significantly lose Foxp3 binding in sgFoxp3 and sgBrd9 (n = 1,699) in sgNT, sgFoxp3, sgBrd9, and sgPbrm1.
(G) As in (E) but for sites that lose H3K27ac (FC 1.5, Poisson p < 0.0001, hypergeometric p of overlap = e−7,938).
(H) As in (F) but for H3K27ac ChIP read density.
(I) As in (D) but for Foxp3 ChIP-seq signals in DMSO- and dBRD9-treated Treg cells at all Foxp3-bound sites in DMSO.
(J) As in (E), but for sites that significantly lose Foxp3 binding in dBRD9 treated Treg cells versus DMSO (FC 1.5, Poisson p < 0.0001).
(K) As in (F) but for DMSO- and dBRD9-treated cells.
(L) As in (F) but for Treg cells transduced with sgNT or sgBrd9, with ectopic expression of the MIGR vector control or Foxp3.
See also Figure S6.