Figure 8.
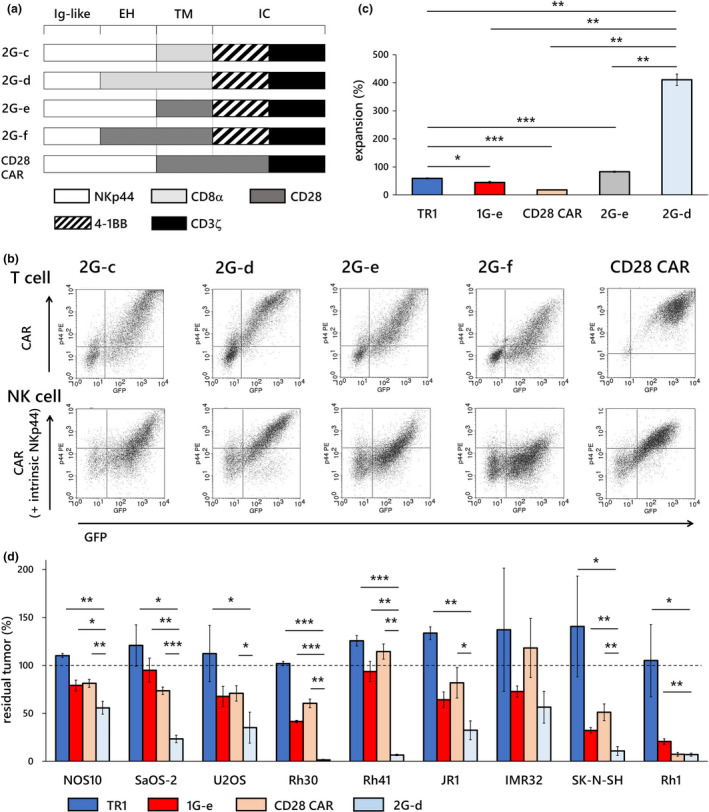
Second‐generation NKp44‐based CAR‐T cells with 4‐1BB co‐stimulation demonstrated excellent proliferation and enhanced anti‐tumor effects. (a) We created an array of second‐generation NKp44‐based CAR constructs that incorporated the 4‐1BB co‐stimulatory domain (2G‐c, 2G‐d, 2G‐e, 2G‐f). We also constructed NKp44‐based CAR with CD28 co‐stimulation that had been reported by Eisenberg et al. 23 (CD28 CAR). (b) Transduction of the CAR construct with CD8α hinge and transmembrane domain, 4‐1BB signalling domain, and CD3ζ (2G‐d) resulted in the highest surface expression on both T cells and NK cells among all the second‐generation 4‐1BB CARs generated. (c) T cells transduced with the construct 2G‐d (pale blue square) showed significantly higher expansion in response to target cell exposure than T cells with non‐signalling CAR (TR1; blue square), T cells transduced with first‐generation CAR (1G‐e; red square), other second‐generation CAR‐T cells with the 4‐1BB co‐stimulatory domain (2G‐e; grey square) and second‐generation CAR with the CD28 co‐stimulatory domain (CD28 CAR; beige square). (d) T cells transduced with our best construct (2G‐d; pale blue square) showed significantly stronger inhibitory effects in long‐term co‐culture assay at E:T ratios of 1:1 against various solid tumor cells than T cells (TR1; blue square), first‐generation NKp44‐based CAR‐T cells (1G‐e; red square) and second‐generation CD28 NKp44‐based CAR‐T cells (CD28 CAR; beige square). The y‐axis shows percentage of residual tumors (as compared with tumor cell without effector cells). Data are means ± SD of three technical replicates. Experiments were independently repeated at least three times, and representative data are shown. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. EH, extracellular hinge domain; IC, intracellular domain; Ig‐like, immunoglobulin‐like domain; TM, transmembrane domain.
