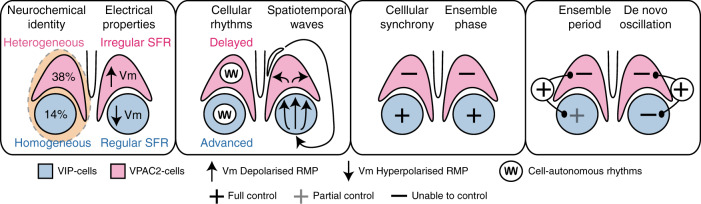
Fig. 9. The VIP-VPAC2 neuropeptidergic axis as a pacemaking hub within the suprachiasmatic nucleus circadian circuit.
Summary diagram showing the cellular properties of the VIP-VPAC2 neuropeptidergic axis and their control of SCN emergent properties. VIP and VPAC2 neurons are neurochemically, electrophysiologically and spatially distinct SCN subpopulations. VIP neurons are phase advanced relative to VPAC2 neurons with a tight spatiotemporal organisation exhibiting dorsal to ventral waves, while the VPAC2 neurons are phase delayed with a looser medial and lateral spatiotemporal distribution. VIP cells can control cellular synchrony, ensemble phase and weakly contribute to ensemble period while VPAC2 cells cannot definitively control any of these emergent properties. However, both populations together are required to exert full pacemaking control and initiation of de novo rhythmicity.