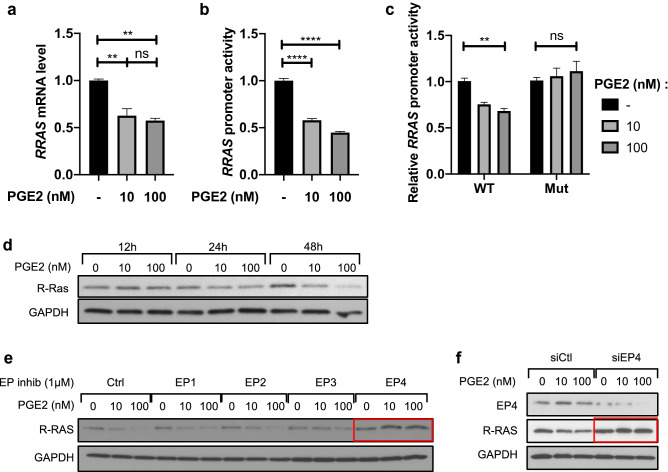
Figure 5.
PGE2 transcriptionally represses RRAS expression in an EP4-dependent manner. (a) HBVPs were treated with PGE2 (10 or 100 nM) or control DMSO for 48 h, and RRAS expression was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR at 48 h post-treatment. The mRNA extracts were pooled from three different cell culture dishes, and the RT-PCR analyses were repeated in two independent experiments and in triplicates. The RRAS mRNA level was normalized to that of cyclophilin A using the delta-delta Ct method. Fold change in RRAS expression is shown relative to the control. (b) In parallel, HBVPs were stably transduced with lentiviral particles delivering a -1907/ + 1 RRAS promoter-reporter construct. Luciferase assay was conducted to determine the promoter activity 48-h post-treatment of HBVPs with the same compounds. Luciferase assay results are shown as means ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in tri- or quadruplicates. (c) The specificity of RRAS promoter activity in response to PGE2 was assessed by transient transfection of 293 T cells with a wild-type (WT) RRAS promoter-reporter construct or a mutated construct (Mut) lacking cyclic AMP-responsive elements (CRE). Renilla luciferase activity was used as an internal control. The results are representative of two transfections performed in triplicates. One-way ANOVA test, **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001; ns: not significant. (d) Time-course western blot analysis of R-Ras expression in HBVPs treated with PGE2 for 12, 24 or 48 h. (e) HBVPs were incubated for 5 h with inhibitors of different EP receptors (EP1: ONO-8713; EP2: PF-04418948; EP3: ONO-AE5-599; EP4: ONO-AE3-208) prior to PGE2 treatment. 72 h later, R-Ras protein expression was analyzed by western blot. (f) EP4 expression was silenced in HBVPs using siRNA. Cells were treated with PGE2 24 h after transfection, and protein extracts were collected 48 h later for western blot. GAPDH was used as a loading control.