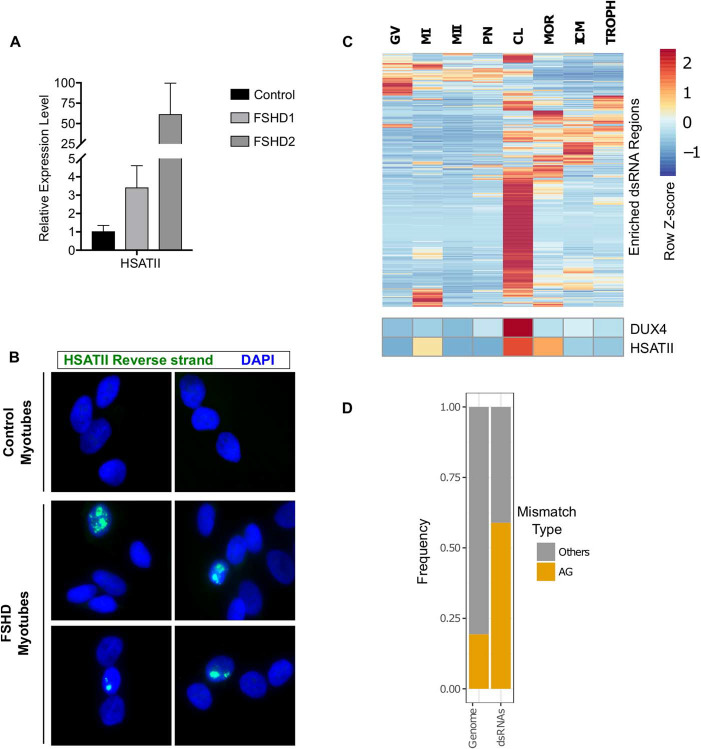
Figure 6. Endogenously expressed DUX4 induces dsRNA forming transcripts, including HSATII. (A) RT-qPCR data showing transcript expression levels of HSATII in control (MB135), FSHD1 (MB073) or FSHD2 (MB200) cells grown in differentiation medium. Data are normalized to RPL27 levels and shown relative to the control cell line. Data are depicted as the mean values of three experiments performed on independent days. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. (B) RNA-FISH using probes targeting the reverse HSATII transcript in control (MB135) or FSHD (MB073) differentiated myotubes. Consistent with rare DUX4 expression in FSHD muscle cells, we observed a small subset of HSATII-positive nuclei in the FSHD cells, but not control cells. Images are representative from two independent experiments conducted on separate days. (C) Heatmap of DUX4-induced dsRNA, DUX4 and HSATII expression across various stages of human embryo development. Read counts were normalized and depicted as the within row z score. Data are from Hendrickson et al. (3). (D) Frequency plot of AG compared to all other possible mismatches in cleavage stage samples from Hendrickson et al. (3). Whole genome refers to all mismatches called, regardless of location and dsRNAs are mismatches called within DUX4-induced dsRNA regions. GV, germinal vesicle; MI, metaphase I; MII, metaphase II; PN, pronuclear stage; CL, cleavage stage; MOR, morula; ICM, inner cell mass; TROPH, trophectoderm.