Figure 6.
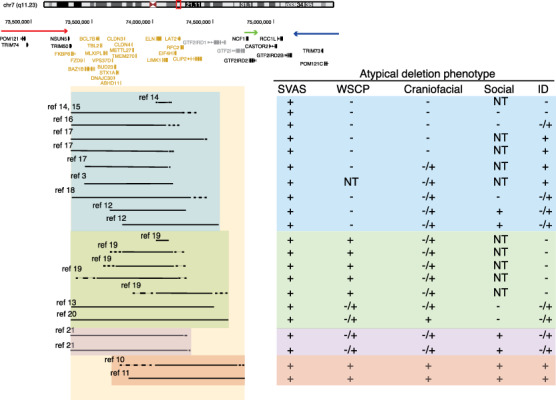
Human atypical deletions support oligogenic contribution of genes in the WSCR to phenotypes. Schematic of the WSCR on chr7q11.23. The arrows indicate the regions of low copy repeats. The typical deletion is demarcated using the yellow box. Atypical deletions demarcated in blue show no contribution to the WSCP. Atypical deletions demarcated in green show contribution to the WSCP. Atypical deletions demarcated in purple provide evidence of deletions that spare GTF2I and GTF2IRD1 that show contributions across phenotypic domains including social behavior. Atypical deletions demarcated in red provide evidence that the telomeric region is sufficient to produce the full spectrum of phenotypes. The large amount of overlap of all deleted regions and the mild phenotypes present across the atypical deletions suggests an oligogenic pattern. SVAS, supravalvular aortic stenosis; WSCP, Williams syndrome cognitive profile; ID, intellectual disability; NT, not tested; −, absent; +, present; −/+, milder than typical WS.
