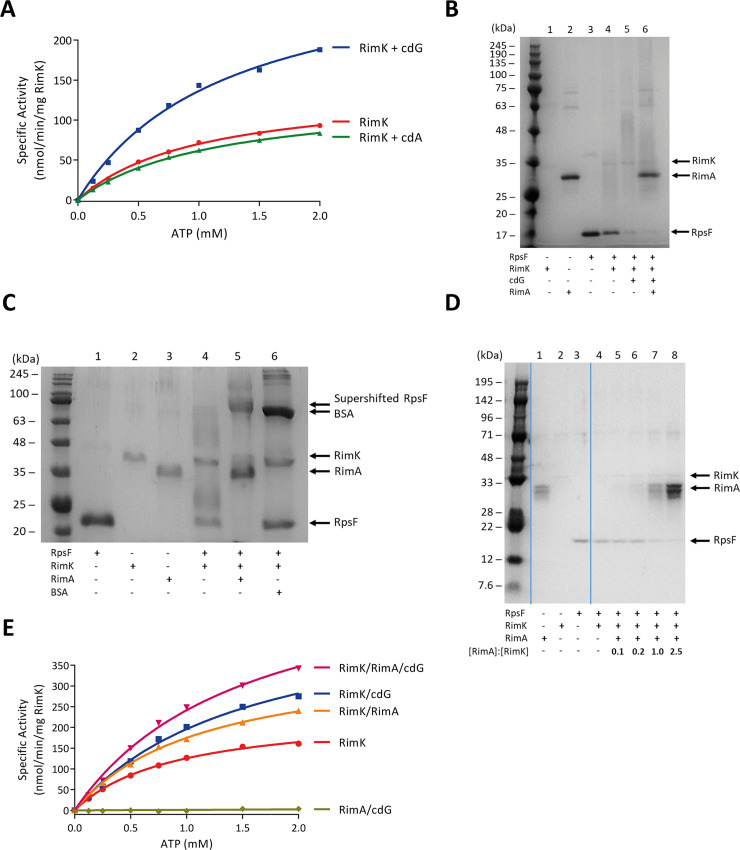
Fig 2.
(A) CdG stimulates RimK ATPase activity. RimK was present at a concentration of 2.5 μM. Nucleotides were present at a concentration of 25 μM. (B) CdG and RimA additively accelerate the rate of RpsF modification. 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. E. coli RpsF, SBW25 RimK and SBW25 RimA were present at a concentration of 6.4 μM, 3.8 μM and 3.9 μM respectively. The positions of RimK, RimA and RpsF are indicated. CdG was present at a concentration of 150 μM. The samples were incubated overnight prior to electrophoresis. Modification of RpsF by RimK is inversely related to the intensity of the indicated RpsF band. (C) RimA alone accelerates the rate of RpsF modification. 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. E. coli RpsF was present at a concentration of 13.6 μM and SBW25 RimK and RimA were present at a concentration of 3.8 μM and 3.9 μM respectively. The position of a super-shifted RpsF band in the penultimate lane and the positions of RimK, RimA, RpsF and BSA are also indicated. The samples were incubated overnight prior to electrophoresis. (D) Equivalent concentrations of RimA are required to stimulate RimK modification activity. Samples were run on a 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. E. coli RpsF was present at a concentration of 6.8 μM, SBW25 RimK at 1.9 μM. RimA was present at the indicated ratio relative to RimK in each case. The positions of RimK, RimA and RpsF are indicated. Samples were incubated for 60 minutes prior to electrophoresis. (E) The ATPase activity of RimK is stimulated additively by RimA and cdG. SBW25 proteins were present at 1 μM. CdG was present at a concentration of 25 μM.