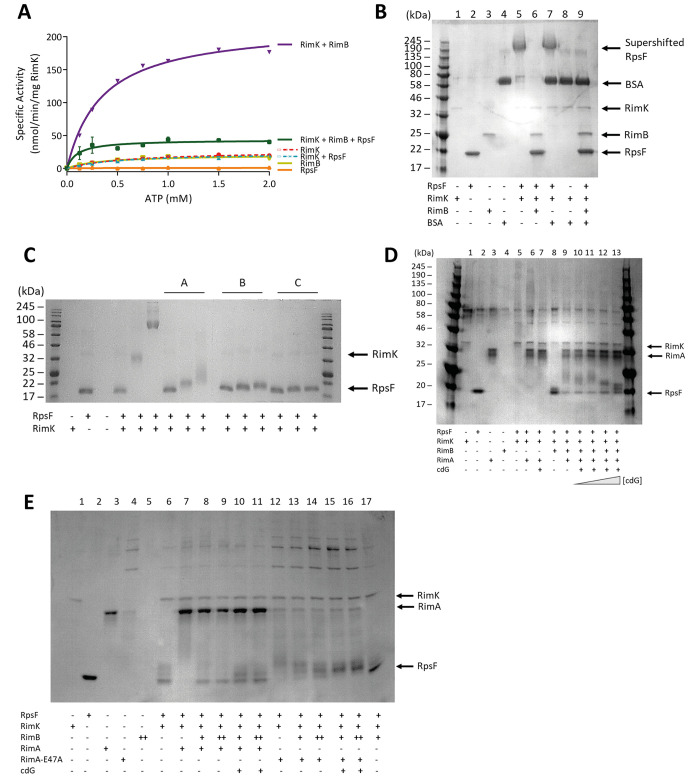
Fig 3.
(A) The presence of RpsF drastically reduces the stimulation of RimK ATPase activity by RimB. E. coli RpsF, SBW25 RimK and SBW25 RimB were present at a concentration of 1 μM. (B) RimB specifically antagonizes RimK modification activity. 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. E. coli RpsF was present at a concentration of 6.8 μM, BSA was present at a concentration of 3.8 μM, SBW25 RimK and RimB were present at a concentration of 7.5 μM and 12 μM respectively. The positions of the supershifted RpsF band, RimK, RpsF, RimB and BSA are indicated. The samples were incubated overnight prior to electrophoresis. (C) Trace concentrations of RimB are sufficient to significantly antagonize modification of RpsF. 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. E. coli RpsF and SBW25 RimK were present at a concentration of 6.8 μM and 3.8 μM respectively. The ratio of RimB to RimK in lanes labelled A, B and C was 1:3, 1:16 and 1:62.5 respectively. The grey triangles represent increasing glutamate concentrations of 0.2 mM, 2 mM and 20 mM. The positions of RimK (barely visible at this concentration) and RpsF prior to modification are indicated. (D) CdG attenuates the ability of RimA to stimulate RimK modification activity in a RimB-dependent manner. 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. E. coli RpsF, SBW25 RimK, SBW25 RimA and SBW25 RimB were present at a concentration of 6.8 μM, 3.8 μM, 3.9 μM and 6.0 μM respectively. The blue triangle represents increasing cdG concentrations of 5, 10, 50 and 200 μM. Lanes 9 and 11 (containing WT RimA) show increasing densities of low molecular weight RpsF species upon addition of cdG. The positions of RimK, RimA and RpsF (prior to modification) are indicated. (E) A CdG binding mutant of RimA is able to fully stimulate RimK modification activity in the presence of the nucleotide. 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel. E. coli RpsF, SBW25 RimK and SBW25 RimA proteins were present at a concentration of 6.8 μM (due to the intractable nature of the protein to purification and the contribution of contaminants to protein quantitation assays, the intensity of the RimA-E47A band is weaker than the RimA wild-type band), 3.8 μM and 3.9 μM respectively where indicated. RimB was present at either 1.7 μM (denoted by a single cross below the gel) or 3.4 μM (denoted by a double cross below the gel). Cyclic-di-GMP is present at a concentration of 200 μM. Lanes 14 and 16 (containing RimA-E47A) reveal loss of the unmodified RpsF band and increasing intensity of larger species upon cdG addition. The positions of RimK, RimA and RpsF (prior to modification) are indicated.