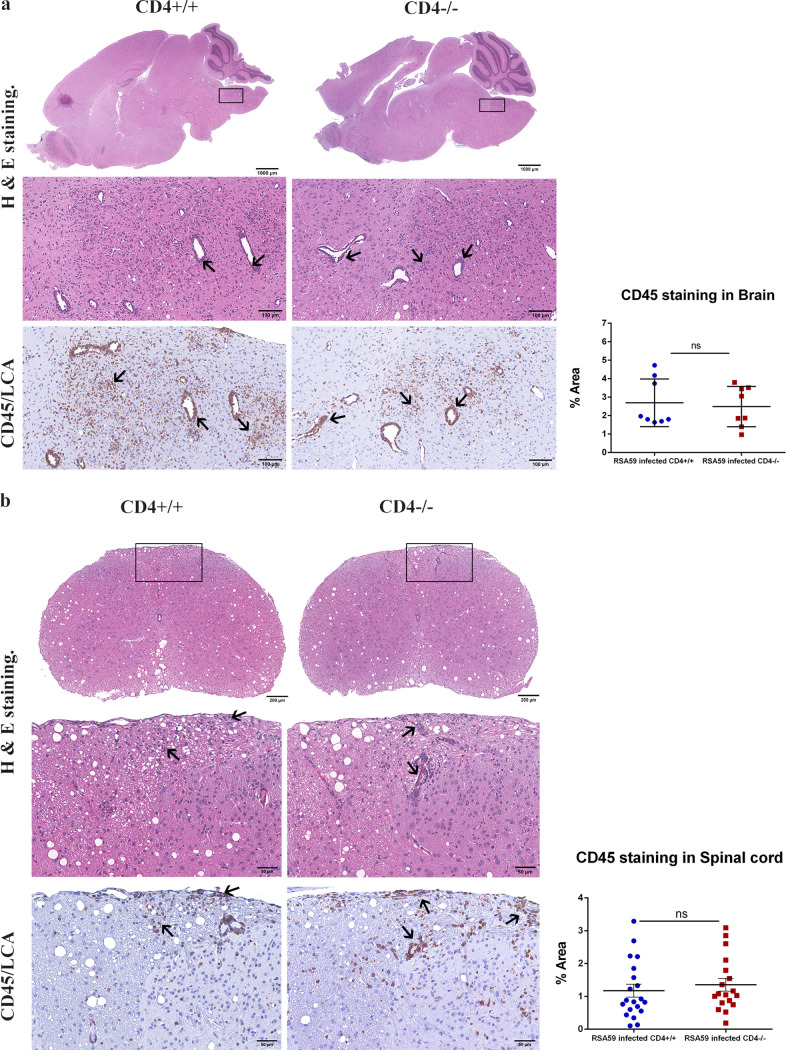
FIG 4.
Absence of CD4 demonstrates no significant changes in encephalomyelitis upon RSA59-induced acute infection. (a and b) (Left) At day 6 p.i., sections of brains (a) and spinal cords (b) from CD4+/+ mice and CD4−/− mice were stained with H&E and immunohistochemically for LCA. The boxed areas are shown at higher magnification below the corresponding brain midsagittal sections (a) or cross sections of spinal cord (b). The arrows in the zoomed sections mark characteristic perivascular cuffing and microglial nodule formation mediated by infiltrating inflammatory cells in the H&E-stained sections which correspond to immunoreactive leukocytes and microglia/macrophages in the CD45 immunohistochemically stained sections. (Right) Quantification of the intensity of staining plotted in scatter diagrams. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t test and Welch correction. The data are presented as means and SEM from 5 independent biological experiments.