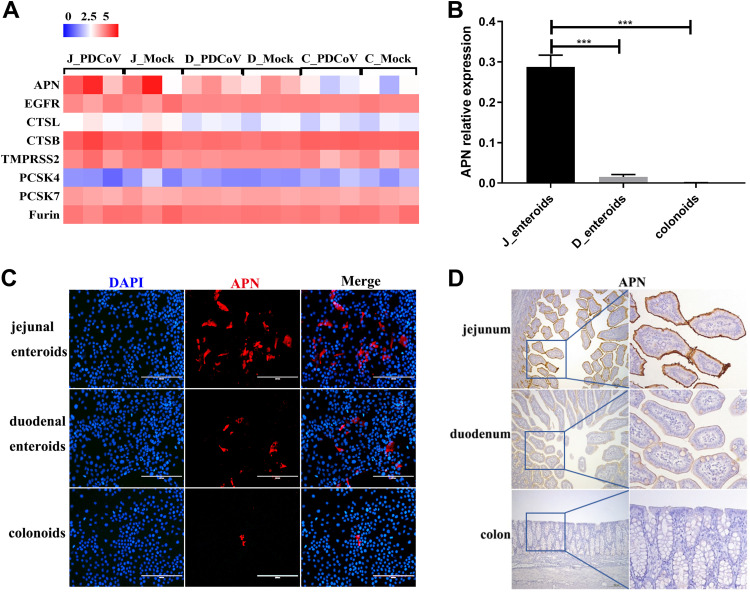
FIG 5.
APN expression mainly determines the differential infectivity of PDCoV in different intestinal segments. (A) Heat map of the APN and coronavirus host proteases expression in enteroids. Enteroid monolayers derived from jejunal, duodenal, and colonic crypts were infected with or without PDCoV for 24 h. Total RNA was isolated from enteroids and used for RNA-seq. Data are based on log(RPKM) values from three independent enteroid preparations. (B) Verification of the APN receptor expression in enteroids by RT-qPCR. Monolayers of jejunal enteroids (J_enteroids), duodenal enteroids (D_enteroids), and colonoids generated from three SPF piglets were cultured for 24 h, and the APN receptor expression level was quantified by RT-qPCR. Data represent the means ±SEMs of results from three wells and three independent enteroid preparations. Error bars denote deviations. ***, P < 0.005. (C) Detection of the APN receptor expression in enteroids by IFA. Monolayers of jejunal enteroids, duodenal enteroids, and colonoids were cultured for 24 h. Cells were fixed and stained with mouse anti-APN monoclonal antibody (red). DAPI-stained nuclei were shown in blue. Scale bar, 200 μm. (D) Detection of APN antigens by an immunohistochemistry assay. Intestinal tissue samples collected from the same SPF piglets were stained with mouse anti-APN monoclonal antibody. Scale bar, 200 μm.