Fig. 2. CHMP1B interlocks in the same arrangement in all structures and flexes at the α3-α4 elbow to accommodate different curvatures.
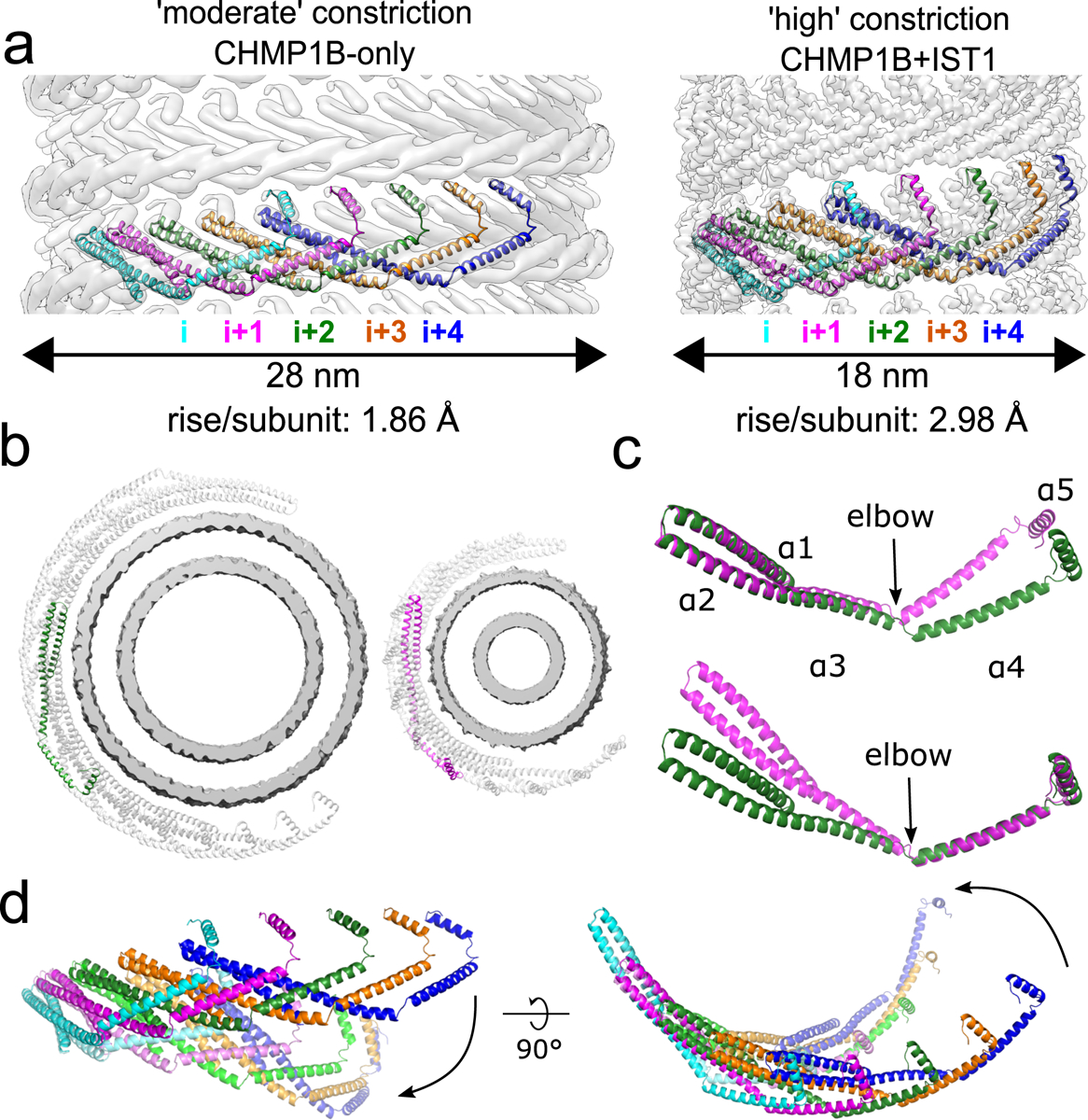
a, CryoEM density maps of CHMP1B from the membrane-bound CHMP1B (left) or right-handed CHMP1B+IST1 (right) filaments. Five interlocked copies of CHMP1B are shown as ribbons. The C-terminal helix α5 of the i protomer always engages helices α1-α2 of the i+4 protomer. The rise per subunit for each helical filament is denoted. b, Comparison of arc curvatures of CHMP1B across the two filaments. Top-down views of half a turn of CHMP1B subunits are shown for either the CHMP1B (left) or CHMP1B+IST1 (right) membrane filaments. The membrane bilayers are shown in grey and the central promoters are shown in green and magenta for the respective filaments. c, Superposition of a CHMP1B protomer from the CHMP1B (green) and CHMP1B+IST1 (magenta) filaments aligned to the CHMP1B N-terminal helices α1-α2 (top) or C-terminal helices α4-α5 (bottom). The biggest conformational change occurs at the elbow joint. d, Superposition of 5 consecutive subunits (colored from left to right in cyan, magenta, green, orange, and blue) of CHMP1B from the CHMP1B (opaque) and the CHMP1B+IST1 (semi-transparent) filament. The respective first protomers from each are aligned as in (c).
