Fig. 3. IST1 polymerization drives constriction of the CHMP1B+IST1 filament.
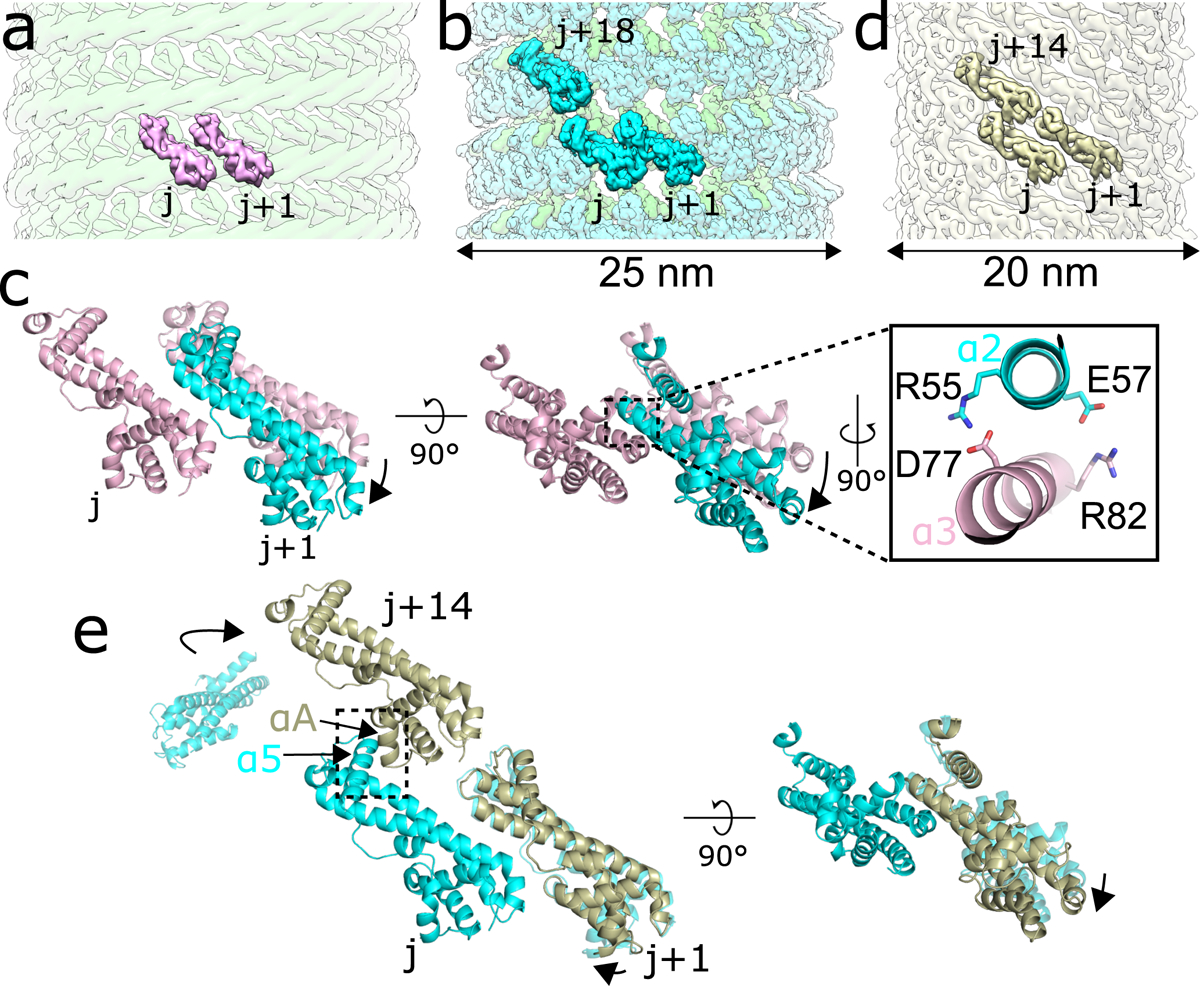
a, Model of two IST1 subunits (j, j+1), colored pink, initially binding onto the CHMP1B filament (green). b, CryoEM reconstruction of the right-handed CHMP1B+IST1 filament, with CHMP1B and IST1 in green and cyan, respectively. Three IST1 subunits (j, j+1, j+18) are highlighted. c, Superposition of the j and j+1 IST1 subunits from (a) and (b), with the j subunits used for alignment. (Inset), new electrostatic interactions between helix α3 (pink) from the j subunit and helix α2 (cyan) from the j+1 subunit help stabilize intra-IST1 contacts to drive constriction. d, CryoEM 3D reconstruction of the IST1NTDR16E/K27E filament (bronze). Three IST1 subunits (j, j+1, j+14) are highlighted. e, Superposition of the j, j+1, and j+14 subunits from the IST1NTDR16E/K27E filament in (d) with IST1 subunits from the CHMP1B+IST1 filament in (b). Protomers were aligned by the j subunit. The boxed area highlights helix α5 of the j subunit and helix αA from the j+14 subunit driving inter-turn interactions.
