Figure 7: Dieldrin does not exacerbate the male-specific PFF-induced loss of ipsilateral nigral TH immunoreactive neurons.
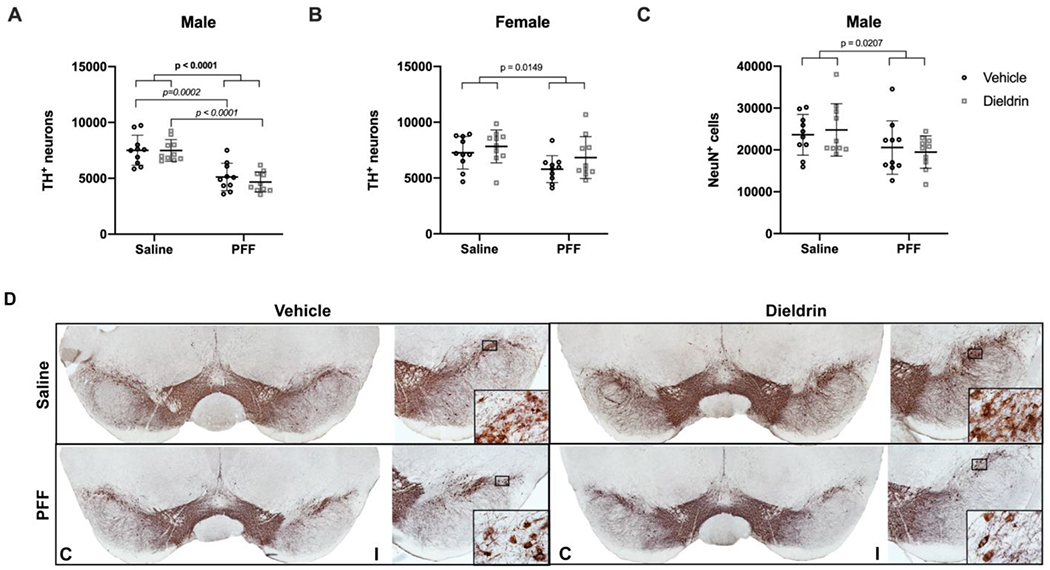
Number of TH+ neurons in the ipsilateral nigra was estimated by unbiased stereology. A) Ipsilateral nigral TH neuron counts in male animals (n = 10 per group) show a PFF-induced loss of TH+ neurons (two-way ANOVA: PFF, p < 0.0001; dieldrin, p = 0.5215; interaction, p = 0.5444). Sidak post-tests show no significant effect of dieldrin, but a significant effect of PFFs in vehicle and dieldrin exposed animals (vehicle:saline vs vehicle:PFF, p = 0.0002; dieldrin:saline vs dieldrin:PFF, p < 0.0001). B) Quantification of ipsilateral nigral TH counts in female animals (n = 10 per group) show a PFF effect (two-way ANOVA: PFF = 0.0149; dieldrin = 0.1061; interaction p = 0.6275). Sidak post-tests show no significant effect of PFFs or dieldrin. The only significant post-test was between dieldrin:saline and vehicle:PFF(p = 0.0304). C) Quantification of ipsilateral nigral NeuN counts in maleanimals (n = 10 per group) show a PFF-induced loss of NeuN (two-way ANOVA: PFF, p = 0.0207; dieldrin, p = 0.9823; interaction, p = 0.5133). Sidak post-tests show no significant effect in any individual comparison. D) Representative images from male animals of nigral TH immunohistochemistry. “C” and “I” indicate contralateral and ipsilateral sides. Data shown as mean+/− 95% CI with significant results of two-way ANOVA indicated on graphs in bold and of Sidak post-tests for dieldrin to vehicle comparisons indicated on graphs in italics. All significant post-test results are reported in this legend.
