Figure 4.
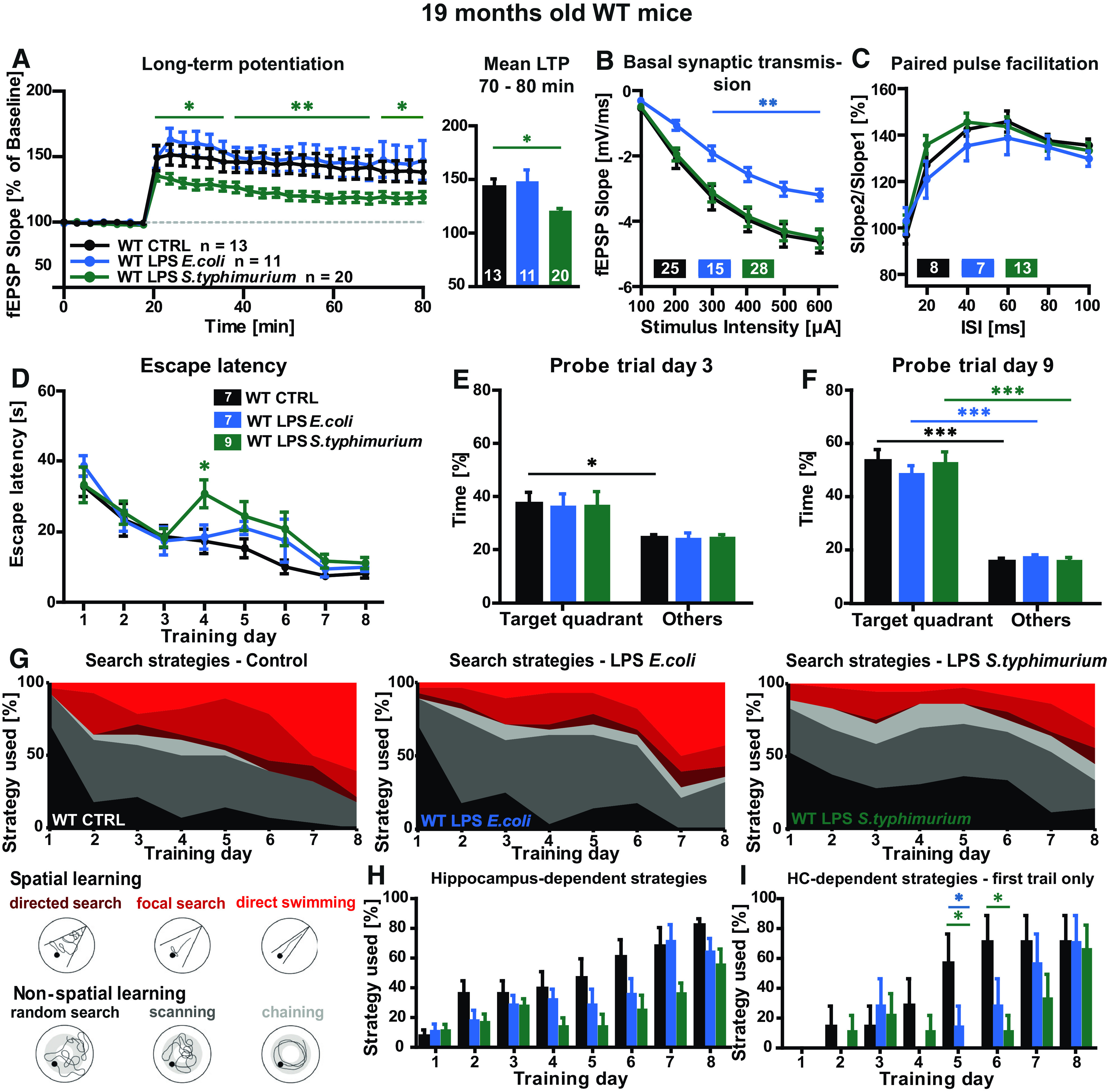
Synaptic plasticity and spatial learning in immune-stimulated aged WT mice. A–C, Short-term and long-term synaptic plasticity at the CA3-CA1 pathway in hippocampal acute slices of aged WT mice three months after peripheral immune stimulation, controls (black), LPS E. coli (0.4 µg/g bodyweight, blue), and LPS S. typhimurium (0.4 µg/g bodyweight, green): (A) LTP induced via TBS after 20 min of baseline recordings and mean LTP fEPSP slope in % for 70–80 min of recording. B, Input-output curve. C, PPF with increasing ISIs; N = 3–4 mice per group, n = 7–28; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. D–I, Nineteen-month-old WT were challenged in the Morris water maze navigation task, controls (black), LPS E. coli (blue), and LPS S. typhimurium (green): (D) escape latency, mean values of four trials per mouse per day. E, F, Target quadrant preference in comparison to time spent in other quadrants during memory reference tests (probe trials) on training day 3 (E) and day 9 (F). G, Illustration and quantification of the six different search strategies random search, scanning, chaining, directed search, focal search, and direct swimming as mean of four trials per mouse per day. H, Quantification of the hippocampus-dependent search strategies for every single training day, mean value of four trials per mouse and day. I, Quantification of the hippocampus-dependent search strategies for every single training day during the first trial; N = 7–9, all data shown as mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001; n = number of mice.
