Figure 3.
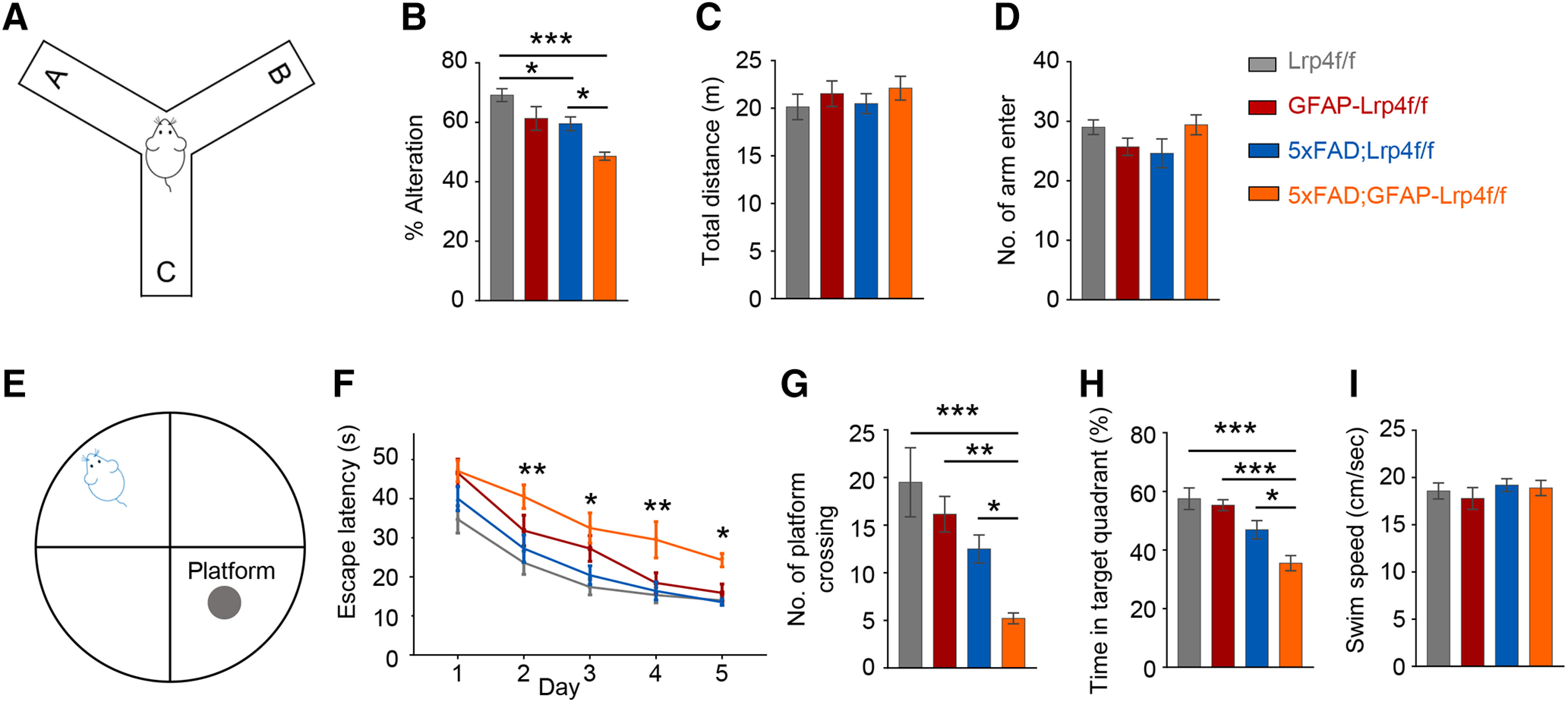
Precipitated cognitive deficits in Lrp4 mutant 5xFAD mice. A, Spatial working memory of Lrp4f/f (n = 13), GFAP-Lrp4f/f (n = 10), 5xFAD;Lrp4f/f (n = 10), and 5xFAD;GFAP-Lrp4f/f (n = 10) was assessed by spontaneous alternation in the Y maze. B, 5xFAD;GFAP-Lrp4f/f further reduced the spontaneous alternation compared with 5xFAD;Lrp4f/f at 6 months: F(3,39) = 11.21, p < 0.0001, ANOVA. C, The total distance explored in the Y maze was not different between the four groups: F(3,39) = 0.5198, p = 0.6711, ANOVA. D, The total number of arm entries was not different in the four groups: F(3,39) = 1.947, p = 0.1380, ANOVA. E, Spatial learning and memory of Lrp4f/f (n = 10), GFAP-Lrp4f/f (n = 13), 5xFAD;Lrp4f/f (n = 15), and 5xFAD;GFAP-Lrp4f/f (n = 12) was assessed in water maze. F-H, Six-mo 5xFAD;GFAP-Lrp4f/f exhibited increase the latency to the hidden platform (F), F(3,230) = 19.6, p < 0.0001, ANOVA; decrease the number of platform crossing (G), F(3,46) = 8.852, p< 0.0001, ANOVA; reduce the time in the target quadrant (H), F(3,46) = 11.35, p < 0.0001, ANOVA, compared with Lrp4f/f and 5xFAD;Lrp4f/f groups. I, Four groups of mice showed similar swim speed in the water maze: F(3,46) = 0.5068, p = 0.6795, ANOVA. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
