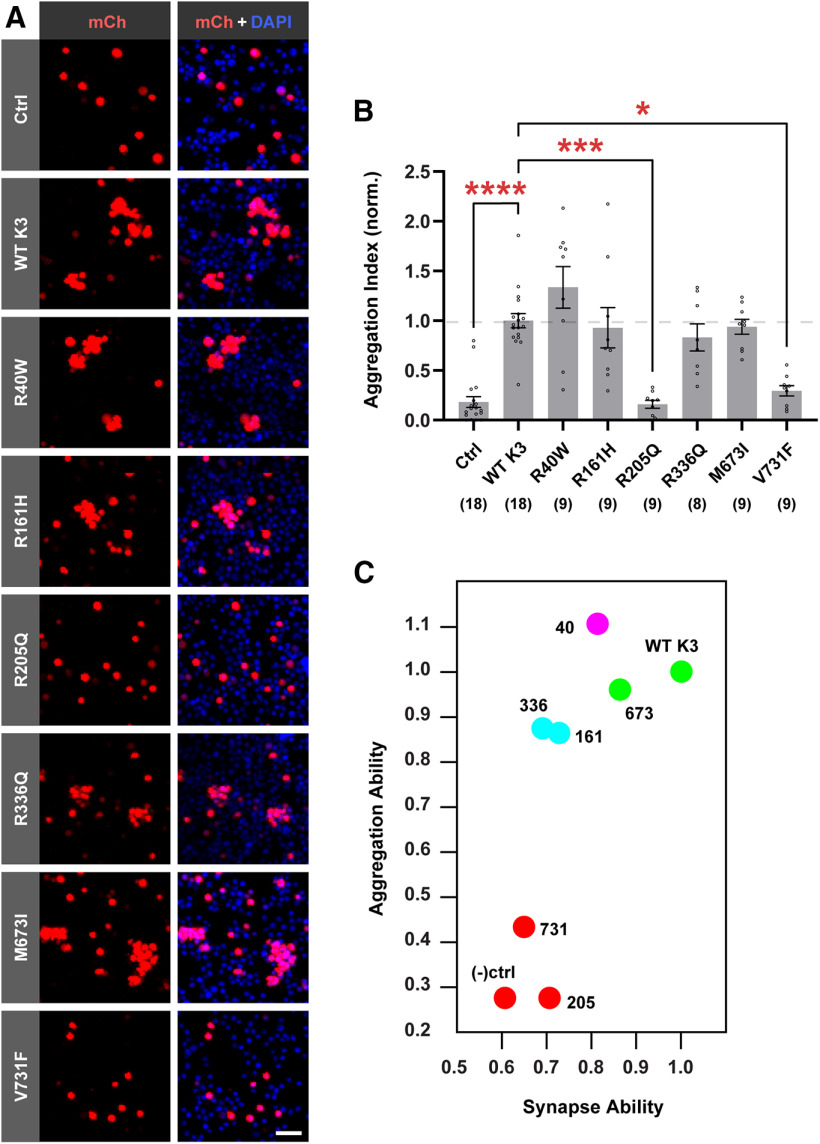
Figure 6.
Synapse-defective R161H and R336Q variants retain transcellular binding. A, Representative images from CHO aggregation assay showing CHO cells transfected with mCherry alone as a negative control (Ctrl), mCherry-2A-Kirrel3-WT (WT K3), or mCherry-2A-Kirrel3 variants. Red represents mCherry (mCh) signal. Blue represents DAPI. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Quantification of CHO cell aggregation assay normalized to WT Kirrel3. n = 8-18 wells (indicated under each bar) from three cultures. *p < 0.05. ***p < 0.001. ****p < 0.0001. For specific p values, see Results. Bar graph shows the mean ± SEM with individual data points represented by open circles. C, k-means clustering of WT Kirrel3, missense variants, and negative control based on their ability to aggregate CHO cells and induce DG presynapse formation using mean rank values normalized to WT Kirrel3 for each condition from the two assays presented in Figures 5B and 6C.