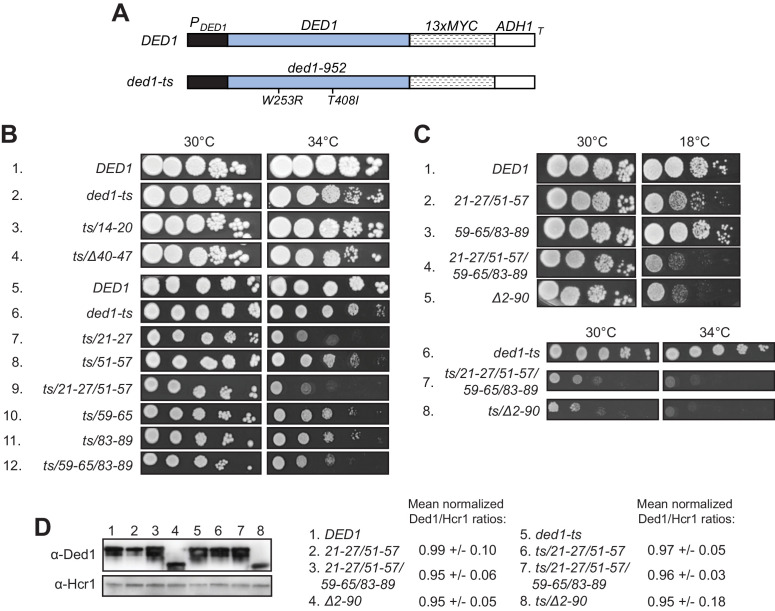
Figure 3. Clustered substitutions of Ded1 NTD residues that impair interaction with eIF4A or eIF4E in vitro confer growth defects in yeast.
(A) Schematics of the myc13-tagged parental DED1 and ded1-ts alleles, expressed from the native DED1 promoter (PDED1) on a single copy (sc) plasmid, used to introduce NTD mutations described in Figure 2A. (B) Mutations substituting single or double binding determinants for eIF4A (21-27; 51-57; 21-27/51-57) or eIF4E (59-65; 83-89; 59-65/83-89) display synthetic temperature sensitivities with the ded1-ts allele of differing severity. Serial dilutions of yeast strains derived from yRP2799 by plasmid-shuffling containing the indicated derivatives of the ded1-ts (rows 2–12), or WT DED1 allele (row 1), on sc LEU2 plasmids (listed in Table 3) were spotted on synthetic complete medium lacking Leu (SC-Leu) and incubated at the indicated temperatures for 2-4d. (C) Disruption of eIF4A and eIF4E binding sites concurrently confers a severe growth defect comparable to that of NTD deletion Δ2–90. Yeast strains harboring the indicated derivatives of DED1 (rows 1–5) or ded1-ts (rows 6–8) were analyzed as in (B). (D) Expression levels of the indicated mutants from (B) or (C) were assessed by Western analysis of WCEs extracted under denaturing conditions with TCA, using the indicated antibodies, following growth in SC-Leu at 18°C for DED1 derivatives and 34°C for ded1-ts derivatives. Ded1/Hcr1 ratios of the indicated derivatives of the WT DED1 or ded1-ts allele were obtained by ImageJ analysis of 3 independent experiments and are normalized to the corresponding parental allele’s Ded1/Hcr1 ratios. This particular blot was atypical in suggesting a reduced level of the ded1-ts-Δ2–90 product.
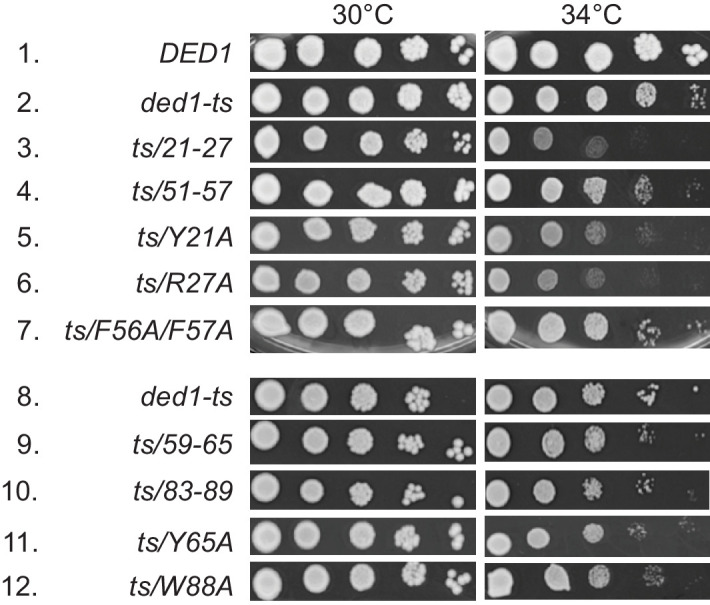
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Substitutions of single Ded1 NTD residues that impair interaction with eIF4A or eIF4E in vitro confer growth defects in yeast.