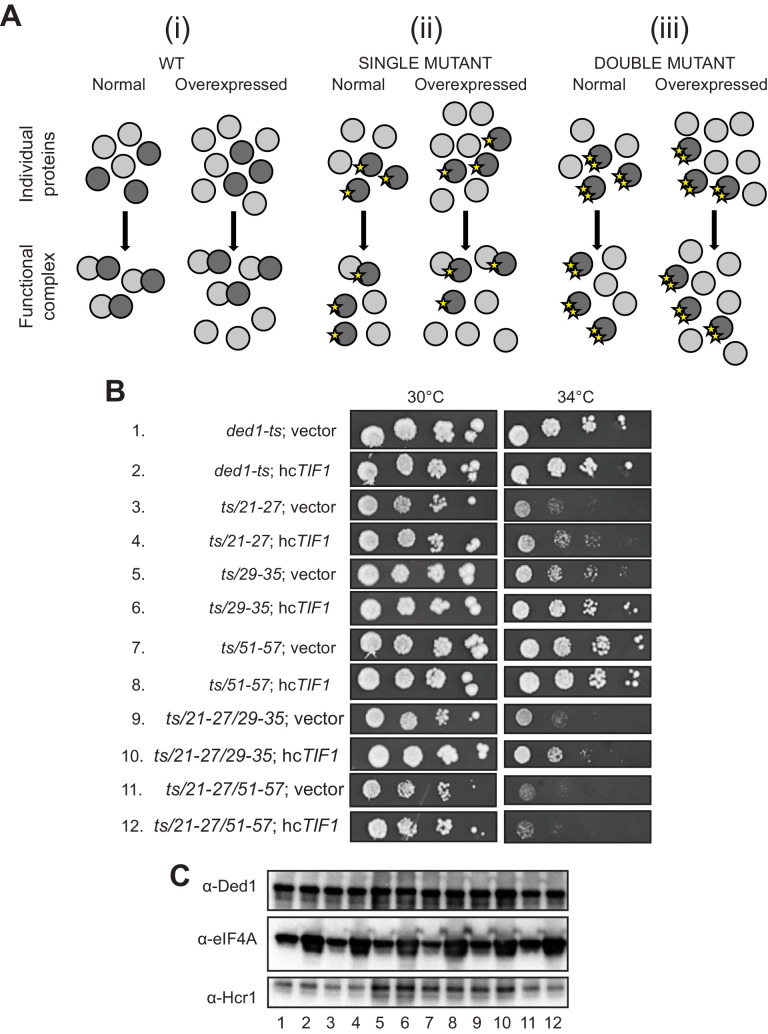
Figure 6. Evidence that Ded1-NTD binding determinants of eIF4A promote cell growth by enhancing eIF4A association.
(A) Schema summarizing expected outcomes for Ded1-eIF4A association based on mass action on overexpressing eIF4A (grey circles) in cells containing different ded1-ts proteins (dark grey circles), as follows: (i) otherwise WT; (ii) a ded1-ts derivative lacking a single binding determinant (single star) that only reduces binding to eIF4A, or (iii) a ded1-ts derivative lacking two binding determinants (double star) that essentially abolishes eIF4A binding. Ded1-eIF4A association depicted by overlapping the circles. (B) Derivatives of strain yRP2799 containing the indicated ded1-ts alleles harboring hcTIF1 plasmid pBAS3432 or empty vector were examined for rates of colony formation at the indicated temperatures as in Figure 3B. (C) Western blot analysis of the strains in (B) conducted as in Figure 3D using the indicated antibodies.