Figure 1. Identification of novel RLC tyrosine phosphorylations sites on myosin RLC by mass spectrometry.
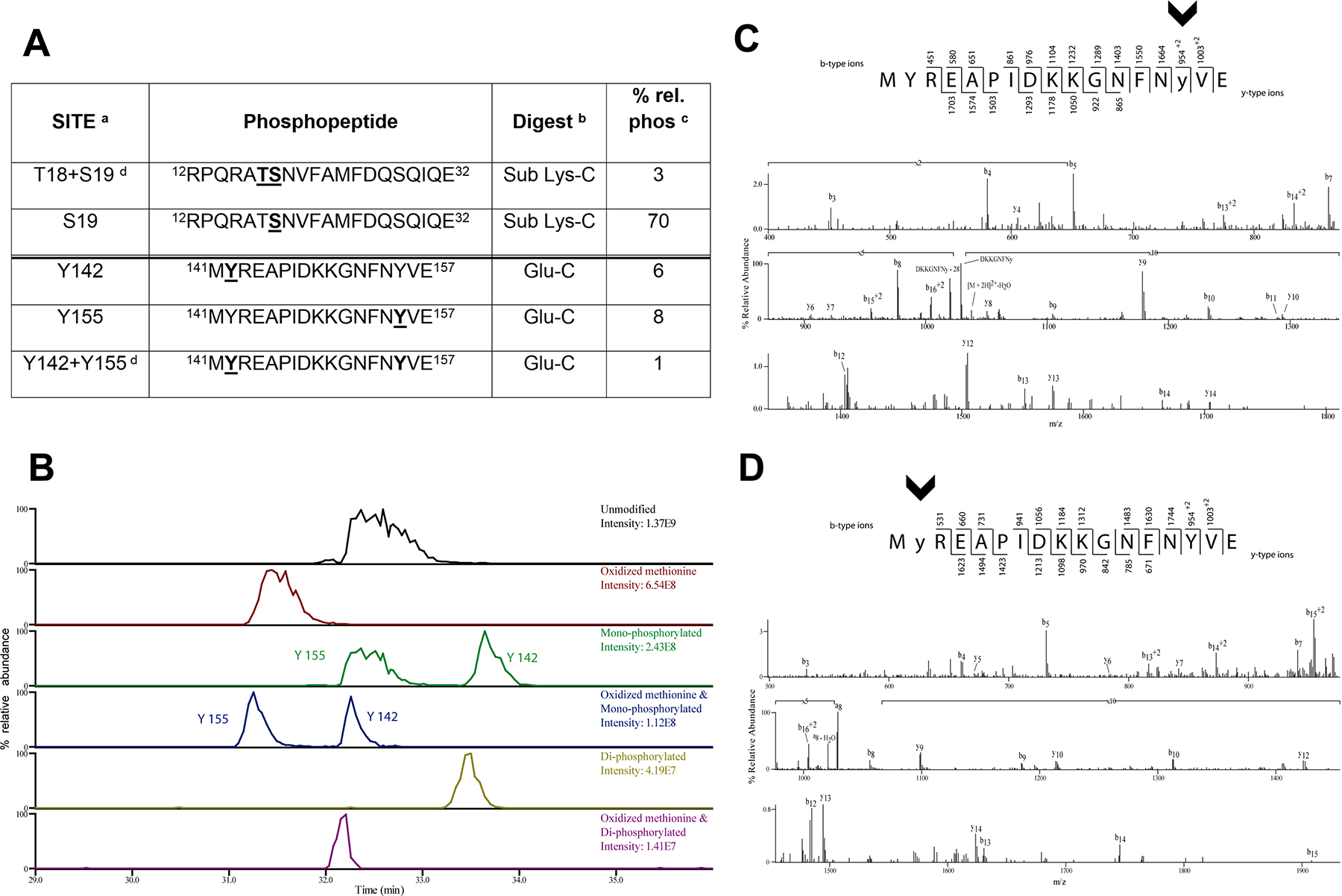
(A) RLC phosphorylated peptides identified by mass spectrometry. Phosphorylated residues are in underlined bold within the sequence. Footnotes: a, the sites of phosphorylation were manually confirmed; b, phosphorylation sites were determined from either peptides generated from the Glu-C digest or from the further digestion with Lys-C; c, relative percent phosphorylation is calculated by dividing the peak area of the phosphorylated form of the peptide over the total peak area of all forms of the peptide; d, there are two bisphosphorylated peptides identified.
(B) The extracted ion chromatograms of the RLC peptide 141-MYREAPIDKKGNFNYVE-157 unmodified, with an oxidized methionine, monophosphorylated with and without oxidized methionine, and bis-phosphorylated with and without oxidized methionine are displayed to show the relative abundance of these species.
(C,D) CAD MS/MS spectra acquired in the ion trap of [M+2H]2+ ion (m/z 1077.99) corresponding to the RLC GluC digest peptide MYREAPIDKKGNFNYVE phosphorylated on Y155 (C) and phosphorylated on Y142 (D). Identified product ions of the b2- and y2- types are listed above and below the peptide sequence, respectively. The identified ions are also indicated in the spectrum and are sufficient to localize the site of phosphorylation (lowercase and arrowheads).
