Figure 4. Y155 is required to generate NMII-dependent front-back polarity and enable cell migration.
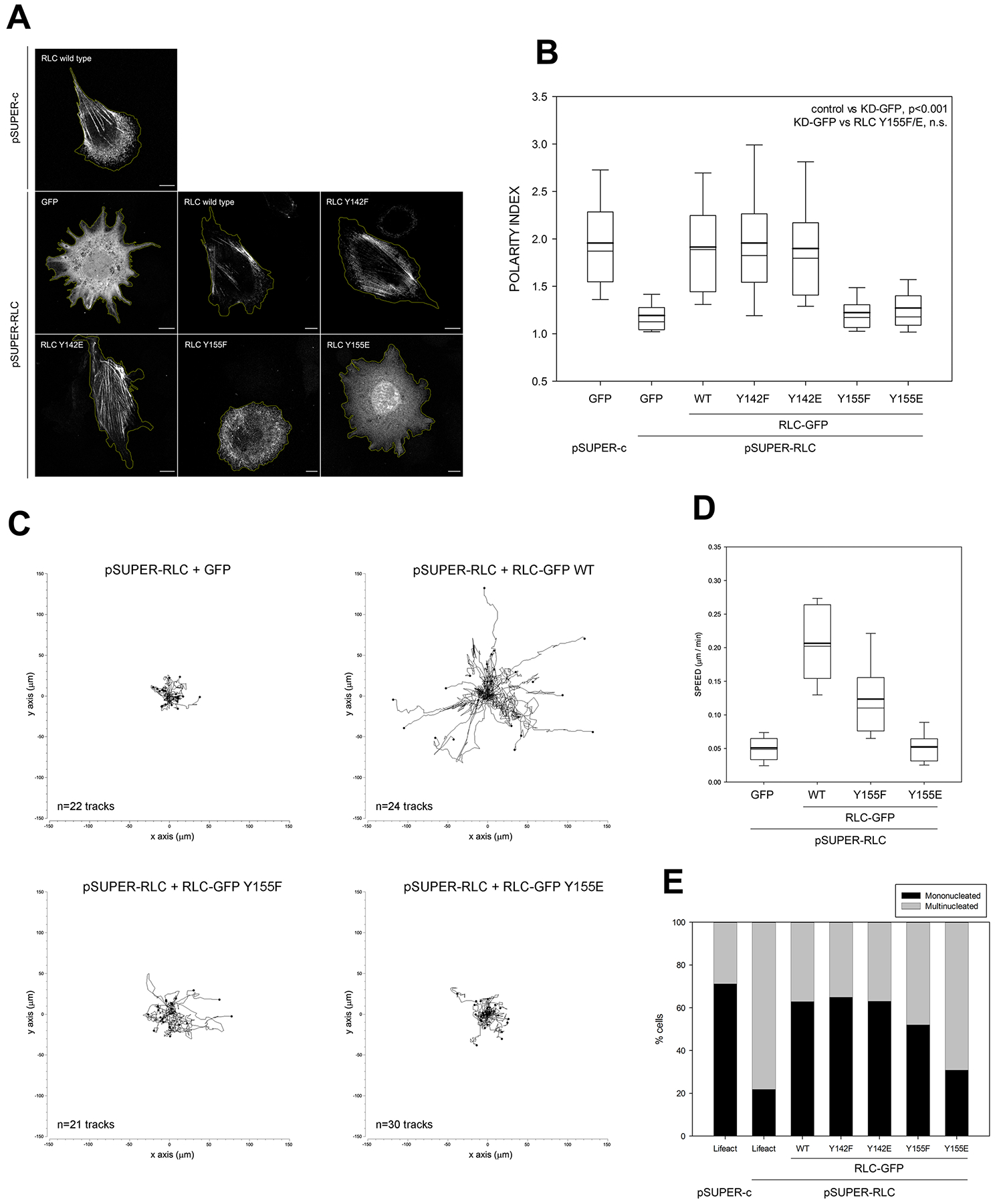
(A) CHO.K1 cells were co-transfected with pSUPER-C and pSUPER-RLC and GFP or the indicated GFP-coupled RLC mutants. After 96h, cells were allowed to adhere to fibronectin for 2h and fixed. Bars=10 μm. Images are representative of >500 examined per condition in three representative experiments.
(B) Quantification of the polarity index as indicated in STAR Methods from three independent experiments. Relevant significances are indicated in the figure.
(C) CHO.K1 cells were transfected with pSUPER-RLC and co-transfected with GFP (control) or GFP-coupled wild type (WT) RLC, Y155F or Y155E mutant as indicated. After 96h, cells were sorted by flow cytometry, adhered to fibronectin-coated coverslips and filmed as they migrate freely for sixteen hours. Data represent the indicated number of tracks from a representative experiment out of three performed.
(D) Speed measurements from the analysis of migratory tracks as shown in (C). All the conditions are significantly different with respect to each other except GFP vs. Y155E.
(E) CHO.K1 cells were transfected with pSUPER-c or pSUPER-RLC and co-transfected with GFP (control) or GFP-coupled wild type (WT) RLC, Y155F or Y155E mutant as indicated, adhered to fibronectin, fixed and stained for lamin A to determine multinucleation. Data include >200 cells/ condition from three independent experiments. All the rescues are statistically significant with respect to the non-rescued condition (second column), except Y155E.
