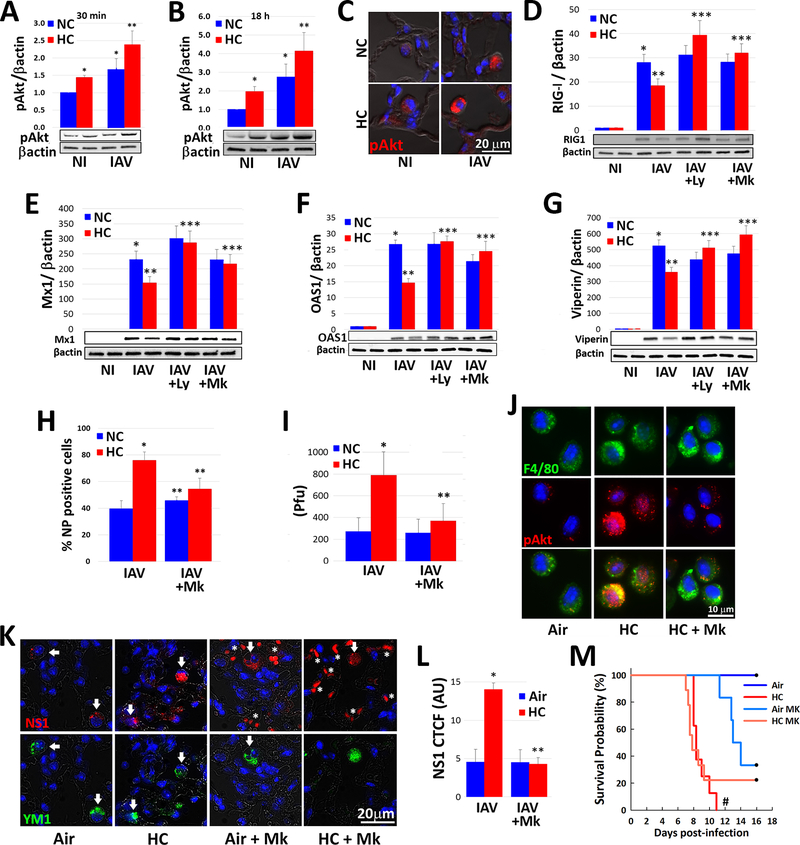
Fig. 4: Hypercapnia potentiates IAV-induced activation of Akt, which mediates hypercapnia-induced suppression of the antiviral response and increased IAV replication in human and mouse macrophages.
Differentiated THP-1 MØs were pre-exposed to 5% CO2 (NC) or 15% CO2 (HC) for 2 h, infected with IAV, and cultured for 30 min (A) or 18 h (B) prior to assessment of Ak1/Akt2/Akt3 phosphorylation at S473/S475/S472 (pAkt) by immunoblot, mean ± SEM, n = 4–6 from at least 4 independent experiments. Additionally, mice pre-exposed to air or normoxic hypercapnia (10% CO2/21% O2, HC) and infected with IAV (30 pfu), as in Fig. 1A were sacrificed at 1 dpi, and Ak1/Akt2/Akt3 phosphorylation at S473/S475/S472 (pAkt, red) was assessed by IF microscopy in lung tissue sections; nuclei were labeled with DAPI (blue), n=3–4, results representative of at least 2 independent experiments (C). THP-1 MØs pre-exposed to NC or HC were also infected with IAV in the absence and presence of the PI3K inhibitor, LY294002 (Ly, 10 μM), or the pan-Akt inhibitor, MK2206 (Mk, 5 μM), and cultured in NC or HC for an additional 18 h, then analyzed for expression of RIG-I (D), Mx1 (E), OAS1 (F) and viperin (G) protein by immunoblot; mean ± SEM, n = 5 from 5 independent experiments, *p<0.05 vs NI; **p<0.05 vs NC + IAV; ***p<0.05 vs HC + IAV. Cells were also immunostained for determination of the percentage of NP-positive cells by IF microscopy (H), and viral titers in culture supernatants were determined by plaque assay (I); mean ± SEM, n = 5 from 5 independent experiments *p<0.05 vs NC + IAV, **p<0.05 vs HC + IAV. Mice were treated with MK2206 (120 mg/kg) or vehicle control by oral gavage were exposed to HC, or air as control for 24 h, then AMØs obtained by BAL were immnostained for phosphorylation of Ak1/Akt2/Akt3 at S473/S475/S472 (pAkt, red); F4/80 (green) was used as MØ marker and nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue), n=3–4, results representative of at least 2 independent experiments (J). Other mice treated with MK2206 or vehicle were exposed to HC for 3 days, or air as control, then infected with IAV (30 pfu/animal) and maintained in air or HC for survival analysis. In addition, mice in each group were sacrificed at 7 dpi, at which point viral NS1 (red) expression in lung tissue sections was assessed; YM1 was used as AMØ marker (green), nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue); white arrows indicate AMØs, asterisks denote autofluorescent RBCs (red) (K), n=5, results representative of at least 2 independent experiments. Viral NS1 protein in AMØs in lung tissue was quantified as corrected total cell fluorescence (CTCF), expressed in arbitrary units (AU); mean ± SEM, n = 5 from at least 2 independent experiments, *p<0.05 vs NC + IAV, **p<0.05 vs HC + IAV (L). Kaplan-Meier plot showing survival after infection (M); mean ± SEM, n = 5 from at least 2 independent experiments, #p<0.05 vs Air + IAV by log-rank test.