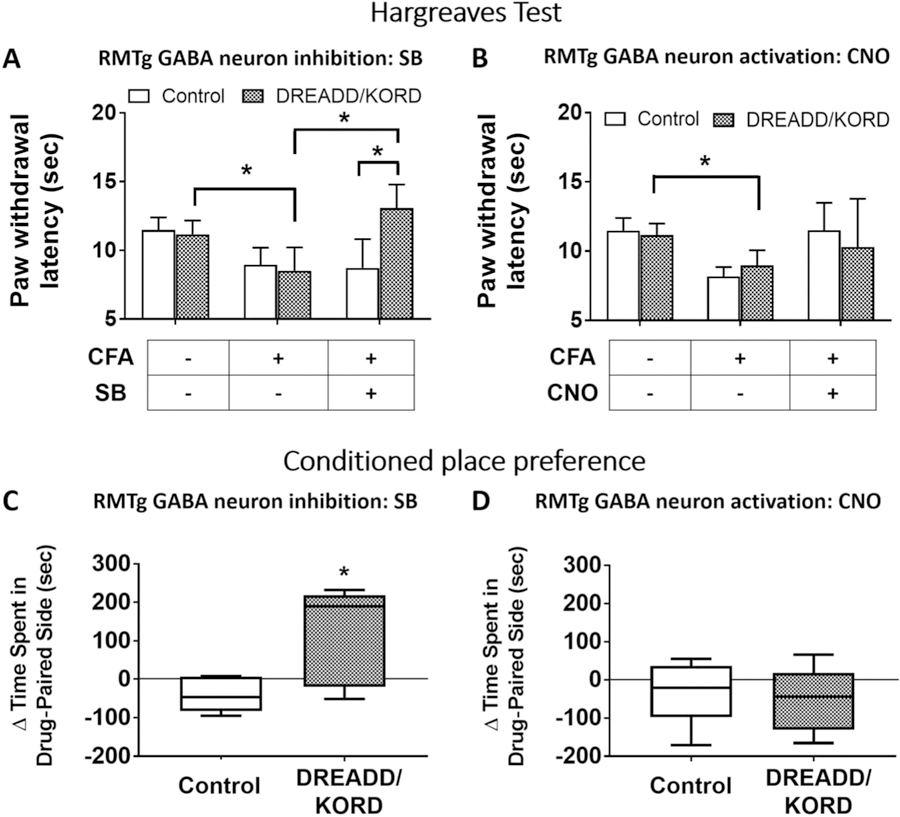
Figure 3.
Direct RMTg GABA neuron inhibition is antinociceptive and diminishes both stimulus-dependent and stimulus-independent inflammatory pain in vGat-cre mice expressing DREADD/KORD in the RMTg, but not in controls lacking the receptors. (A) Salvinorin-B (SB) increases paw withdrawal latency in mice with CFA-induced ankle joint inflammation that express KORD in the RMTg. Mean (±95% CI). (B) Clozapine-N-oxide (CNO) has no effect on paw withdrawal latency in mice with CFA-induced ankle joint inflammation that express hM3 DREADD in the RMTg. Mean (±95% CI). *P < 0.01, paired t tests with the Holm–Sidak correction for multiple comparisons. (C) A conditioned place preference developed to SB in mice with CFA-induced ankle joint inflammatory pain in which RMTg GABA neurons were inhibited. Median (±95% CI). (D) A conditioned place preference did not develop to CNO in mice with CFA-induced ankle joint inflammatory pain in which RMTg GABA neurons were excited. Median (±95% CI), *P < 0.01, t tests with the Holm–Sidak correction. CFA, complete Freund adjuvant; CI, confidence interval; RMTg, rostromedial tegmental nucleus.